Please help keep the Geographer Online a FREE resource
Biomes
Lesson 1: Environments

- To define what the word ‘ecosystem’ means.
- To use the atlas to locate the major world ecosystems, developing their locational knowledge and maps skills.
- To infer what these places look like.

Define the key terms of this unit.
Key terms:
- Ecosystem: An ecosystem is a unit made up of living things and their non-living environment. They have different climates and vegetation.
- Biotic: Living things (plants and animals).
- Abiotic: Non-living things (soil, climate).
- Food web: A series of organisms related by predator-prey and consumer-resource interactions.
- Niche: The special role a plant or animal has in the ecosystem.
- Habitat: the natural environment of an organism; place that is natural for the life and growth of an organism.
|
| ||||||||||||
Ecosystems from Steven Heath
| Ecosystems | |
| File Size: | 1160 kb |
| File Type: | ppt |

Watch the following videos as a summary and review of what we have learnt today.
Lesson 2&3: Tropical Rainforests

- To know the biotic and abiotic components of the Tropical Rainforest
- To understand which components are found in each layer of the Tropical Rainforest

Discuss:
Has anyone in the class been to a rainforest?
What was it like?
What were your first impressions?
Watch the following YouTube to provide a give an overall view of what rainforests are like.
Has anyone in the class been to a rainforest?
What was it like?
What were your first impressions?
Watch the following YouTube to provide a give an overall view of what rainforests are like.
In the student notebooks cut and stick the:
- Rainforest distribution map and colour it in.
- Rainforest Structure diagram and then complete all the layers of the rainforests with annotations.
| Rainforest Structure diagram | |
| File Size: | 123 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
Rainforests from Steven Heath
| Rainforest information | |
| File Size: | 761 kb |
| File Type: | ppt |

Watch Planet Earth 2 Complete the interesting facts worksheet |
| ||||||
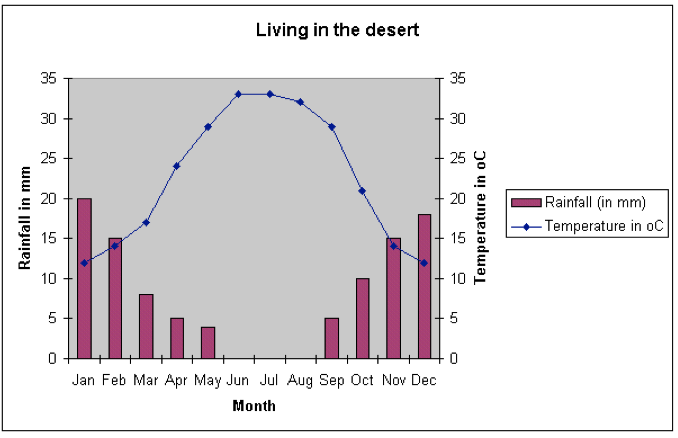
Lesson 4: Desert Climate & Location
|
Cut and glue the Major Deserts on Earth worksheet into your notebooks.
| |||||||||||||||
Lesson 5: Desert Adaptations
|
Print out the following worksheet and in small groups discuss the order and how these items might help you survive in a desert environment.
Extension:
| ||||||||||
|
Using the Worksheet on adaptations discuss in groups how these animals have adapted to their environment.
| |||||||
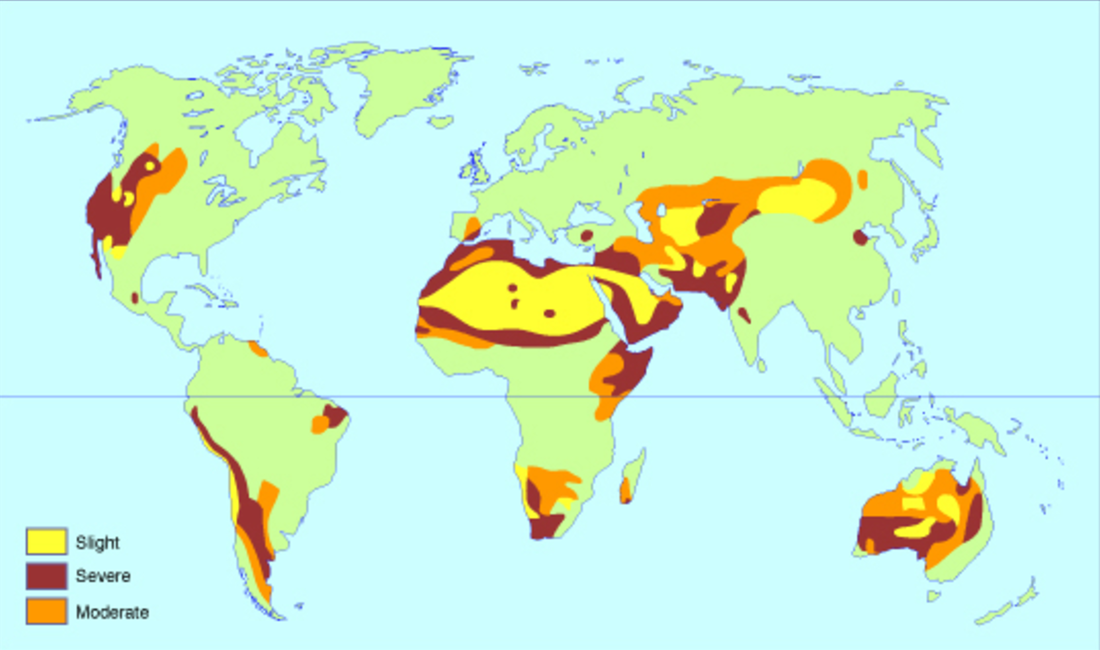
Lesson 6-8: Desertification
|
Using the following video answer the following questions:
|
|
You will be creating a presentation explaining the causes and effects of desertification on the world. Watch the YouTubes below as an introduction into the topic.
| |||||||||||