Please help keep the Geographer Online a FREE resource
Rivers
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| rivers.pdf | |
| File Size: | 145 kb |
| File Type: | |
Water Cyle
|
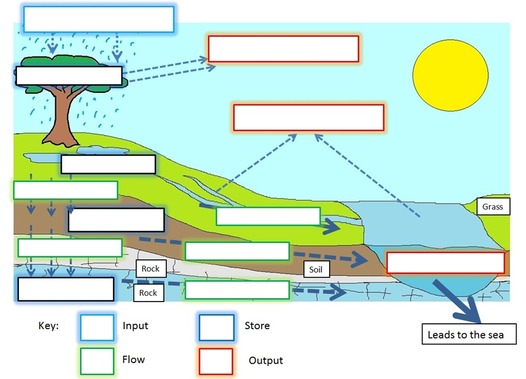
Complete the water cycle diagram and worksheet
| |||||||
|
|
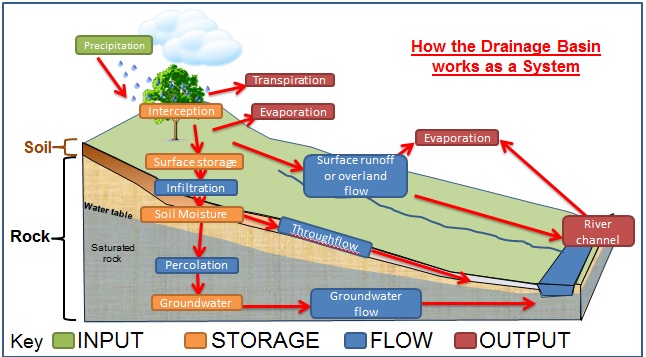
How does the water cycle work?
The major stores of water are the ocean, ice caps, land and the atmosphere. The movement of water between these stores is called transfers. |
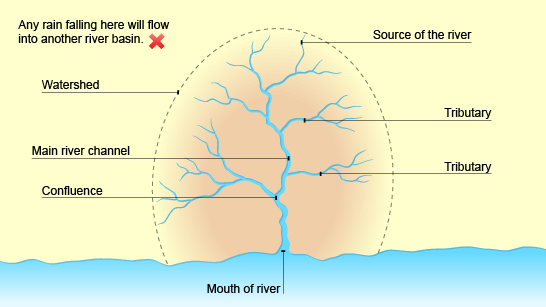
Drainage Basin
River Processes
|
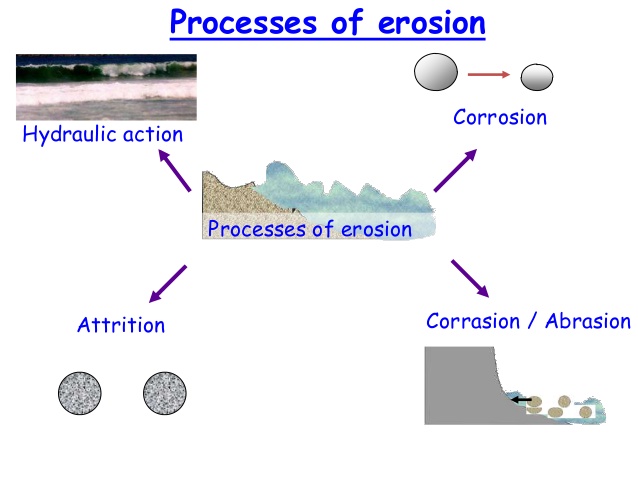
The River processes are the same as we looked at in the Unit of Coasts. You have already learnt this so all you need to do is remind yourself of the forms of Erosion and Transportation that you have looked at.
|
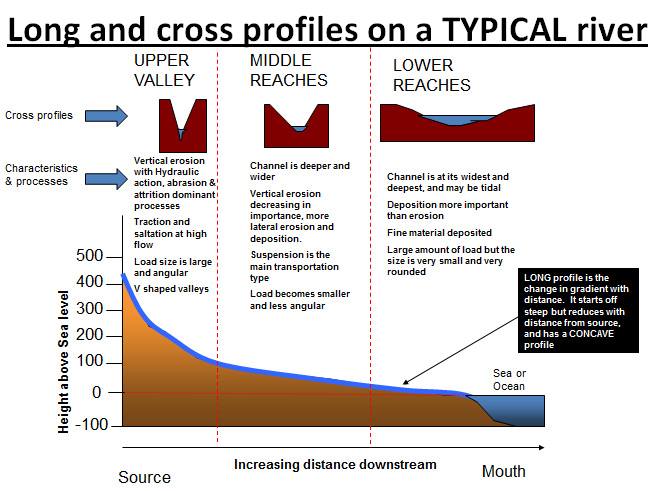
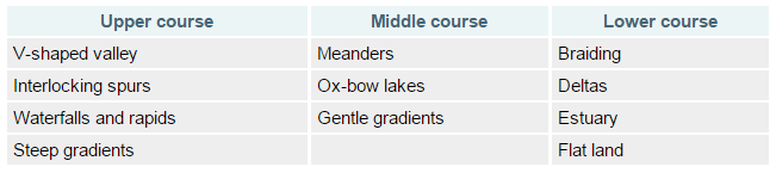
Long River profile
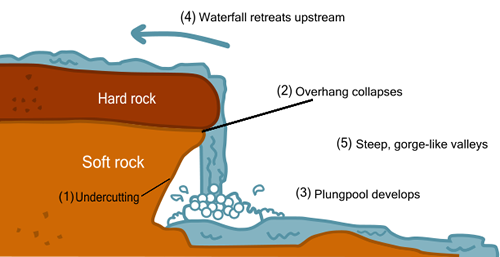
Waterfalls
|
Formation of a waterfall:
|
|
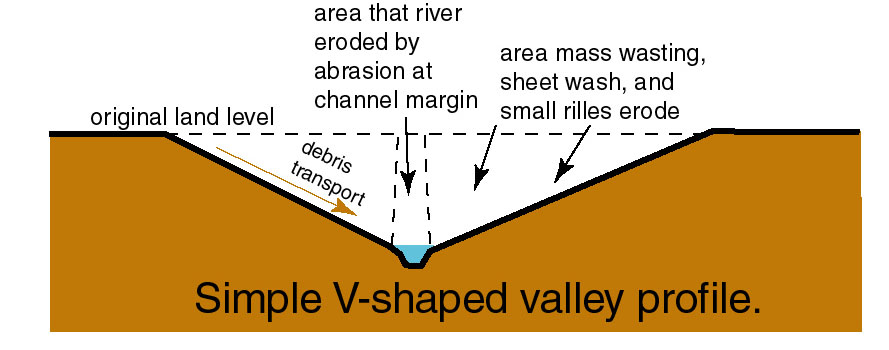
V-Shaped Valleys & Interlocking Spurs
|
When a river is near its source, it often develops a V-shaped valley as the river erodes down (this is called vertical erosion). At the same time, weathering breaks up material on the valley slopes. Weathered material from the valley sides gets deposited in the river. This material is carried by the river and erodes the riverbed through abrasion.
|
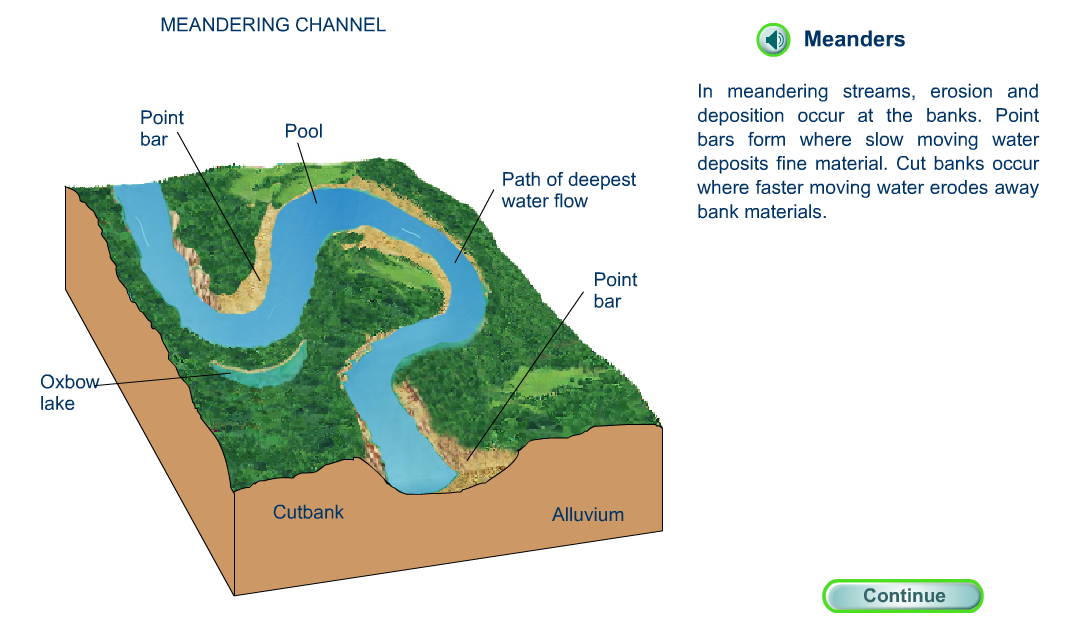
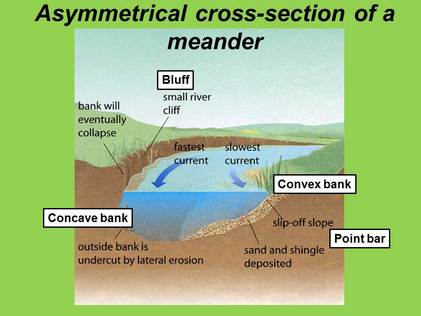
Meanders and Oxbow Lakes

Meander: is a bend in the river. Meanders usually occur in the middle or lower course, and are formed by erosion and deposition.
|
|
|
|
|
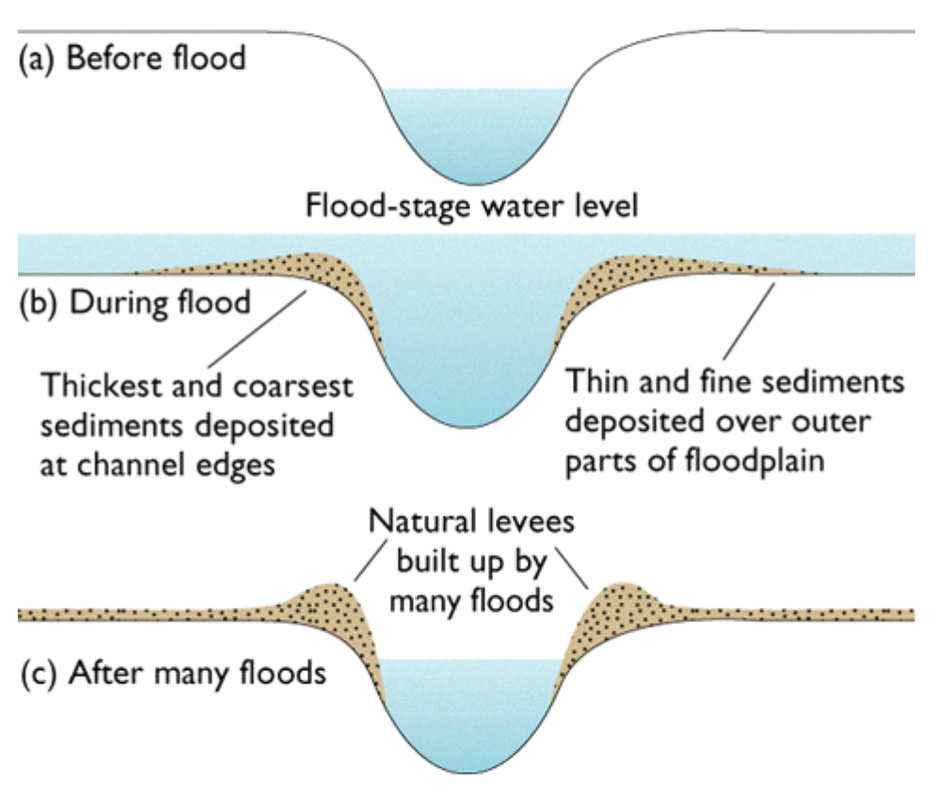
Floodplains
Levees
River Deltas
|
Print and complete the River Delta Worksheet
| |||||||
Why do people live near rivers?
Benefits
Floodplains are dynamic natural systems. The natural processes of periodic flooding, accompanied by erosion and deposition, bring changes to the topography, soils, vegetation, and physical features (such as meanders, braided channels and oxbow lakes) within these areas over time.
Floodplains provide a wide range of benefits to the ecosystem and community that include:
Floodplains are dynamic natural systems. The natural processes of periodic flooding, accompanied by erosion and deposition, bring changes to the topography, soils, vegetation, and physical features (such as meanders, braided channels and oxbow lakes) within these areas over time.
Floodplains provide a wide range of benefits to the ecosystem and community that include:
- Flood storage and erosion control–offer a broad area for streams and rivers to spread out and accommodate temporary storage of flood water, reducing flood peaks and erosion potential
- Water quality maintenance – reducing sediment loads, filtering nutrients and impurities, and moderating water temperature
- Groundwater recharge
- Biological productivity – providing fertile soils with high rate of plant growth and diversity, richer agricultural harvests, and healthier forests
- Habitat for a variety of fish and wildlife, including rare and endangered species
- Recreational opportunities – providing areas for active and passive activities, supporting the economic base
- Open space
Causes of Floods
| Storm Hydrograph | |
| File Size: | 4523 kb |
| File Type: | pptx |
|
Create a brief Video using a hand drawn model explaining:
What a storm Hydro-graph is and how it works. What factors, Physical and Human cause flooding. |
River Management Strategies
|
Using the following three websites create a table listing, describing and explaining the possible management strategies for rivers and their floodplains. Separate them into Hard and Soft Engineering strategies.
|
River Flood Case STudy
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| case_study_mississippi.pdf | |
| File Size: | 7311 kb |
| File Type: | |