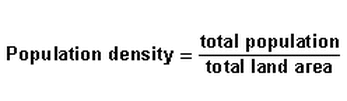Population
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| Population dynamics | |
| File Size: | 145 kb |
| File Type: | |
Population Dynamics
|
Complete the worksheet below.
| |||||||
|
Why has the population grown so quickly?
In small groups discuss this and create a spider diagram with your reason. Do this collaboratively using Coggle. |
Should we be worried?
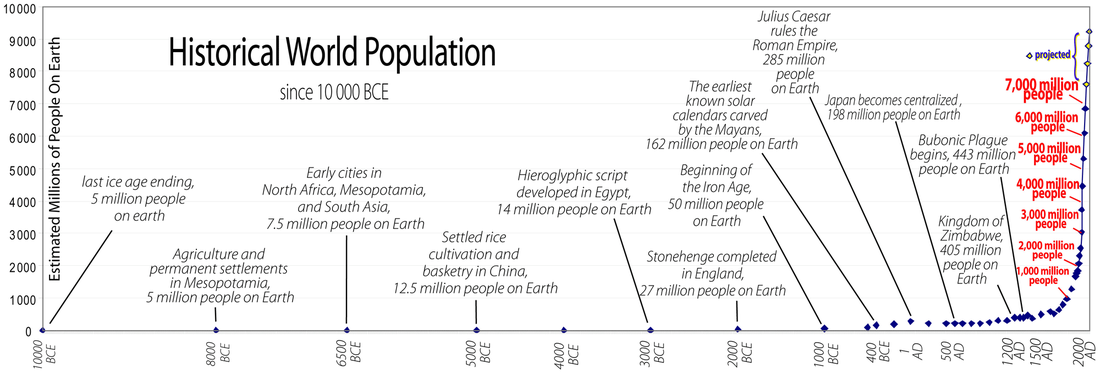
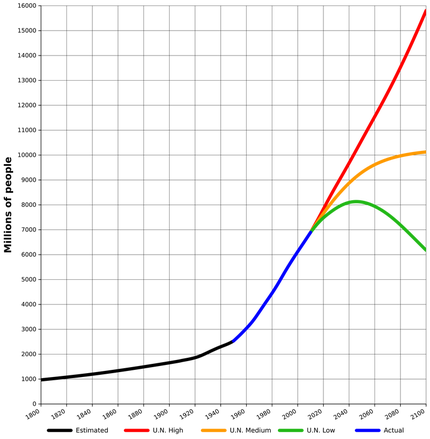
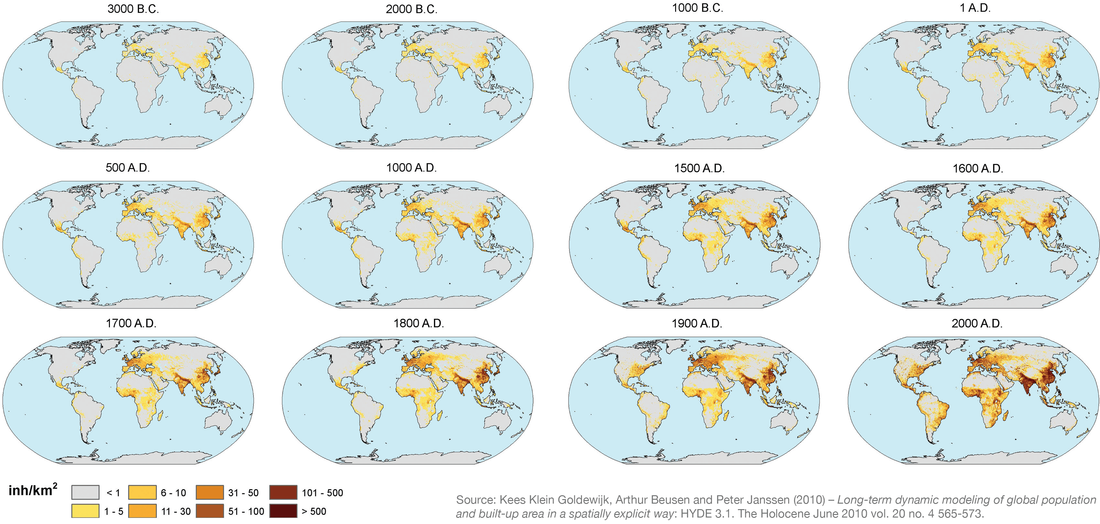
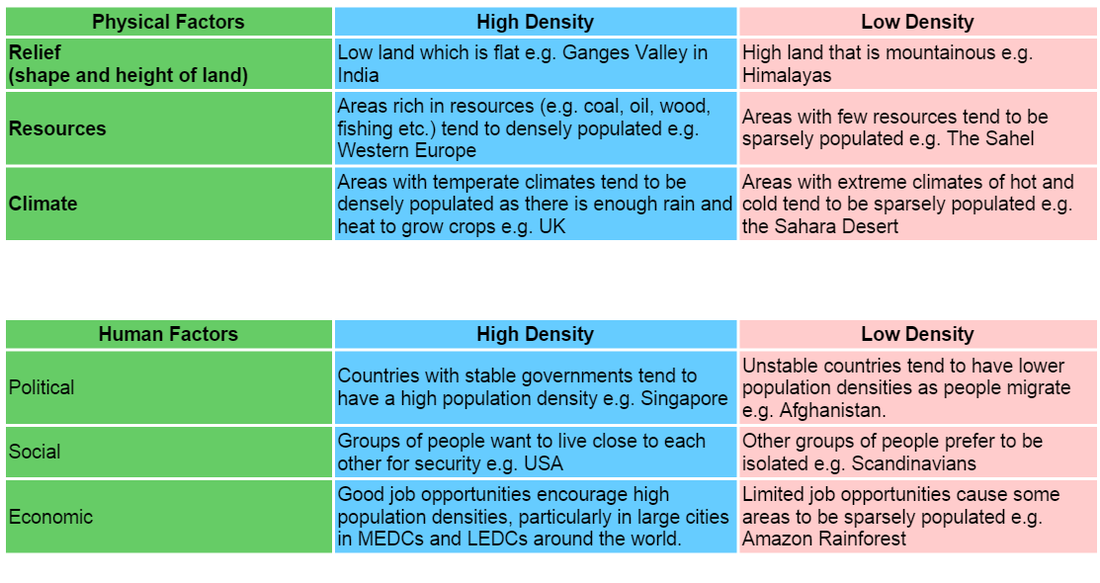
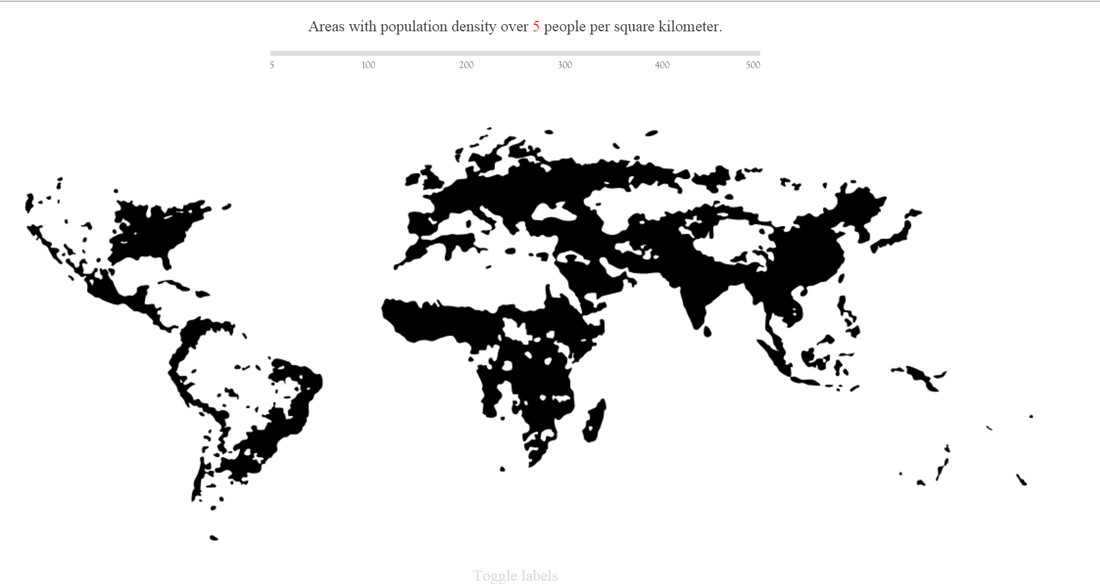
Population Density and Distribution
optimum populations
Population density: The amount of people living in an area of land.
- Many people in a small area = densely populated
- Few people in a large area = sparsely populated
Optimum population: The population is such that it can maximise the benefits from the resources available. It is only when we have optimum population that the quality of life is maximised.
Over population: The resources cannot sustain the current population. As long as there is over population the quality of life will decline through unemployment, pollution, degradation of the environment.
Under population: The population cannot fully utilise the resources available. Quality of life can only slowly be improved. An increase in population would lead to an increase in quality of life.
Create a table and discuss what areas are likely to be over populated and under populated. Why is this the case?
Use the following website to help answer this question.
Use the following website to help answer this question.
|
Discussing Densely and Sparsely populated areas:
| |||||||
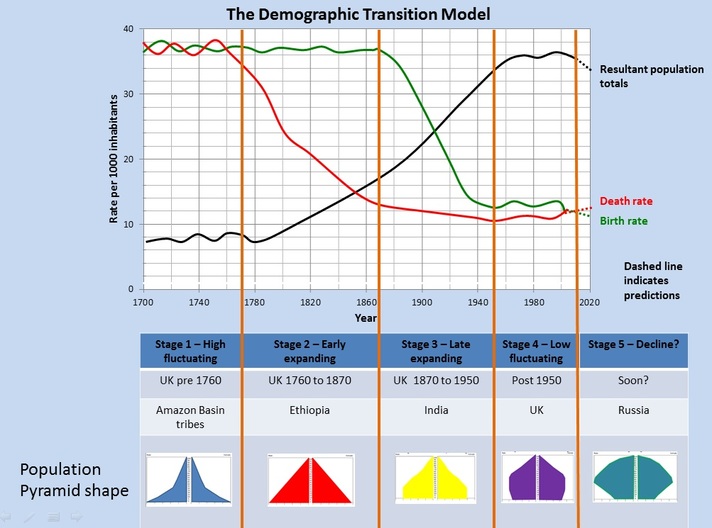
The Demographic Transition Model
Birth Rate – Number of births, per year, per 1000 people in the population
Death Rate – Number of deaths per year, per 1000 people in the population
Life Expectancy – The average number of years a person at birth can expect to live
Natural Increase - An increase in a country's population because birth-rates are higher than death-rates.
Natural Decrease - A decrease in a country's population because death-rates are higher than birth-rates
Death Rate – Number of deaths per year, per 1000 people in the population
Life Expectancy – The average number of years a person at birth can expect to live
Natural Increase - An increase in a country's population because birth-rates are higher than death-rates.
Natural Decrease - A decrease in a country's population because death-rates are higher than birth-rates
|
Draw, label and explain the DTM. To be done on the board together with the class.
|

Create a table (Advantages and Disadvantages) using this Prezi fill in all the reasons.
Population Case Studies
For all the case studies below (pages 11-16)
- Locate the country
- Provide factual evidence
- Explain what factors (climate, relief, location, opportunities, natural resources) help cause this?
- What problems/advantages can this population growth cause the county?
- Answer the specific questions
- Kenya – a country with a high rate of population growth
1 The increase in Kenya’s population between 1969 and 2009.
2 The number of births per woman.
3 The infant mortality rate.
4 Life expectancy.
5 The population forecast for 2030.
6 The percentage of the population under 15.
7 The percentage of the population living in rural areas.
8 The process of unemployed people moving from the countryside to towns and
cities.
9 The World Bank forecast for Kenya’s population in 2030.
10 The fall in the poverty rate between 2005 and 2012.
- Population decline in Russia
1 The birth rate in Russia.
2 The death rate.
3 The year when Russia’s population reached its highest level.
4 The population density.
5 The gender with the highest death rate.
6 The level of use of contraception by married women aged 15–49.
7 The difference in life expectancy between men and women.
8 The greater number of women than men in Russia.
9 The number of villages abandoned since 2002.
10 The medal awarded to families with four or more children.
- Bangladesh – an overpopulated country
1 The population of Bangladesh.
2 The population density.
3 The rate of natural increase.
4 The percentage of the population underemployed.
5 The three major river oodplains.
6 The capital city.
7 The amount of cultivable land lost each year due to urbanisation,
industrialisation and the expansion of infrastructure.
8 The population density of Dhaka.
9 The position of Bangladesh on the 2012 Human Development Index.
10 The change in the incidence of poverty between 2000 and 2010.
- Australia – an underpopulated country
1 The population of Australia.
2 The population forecast for 2025.
3 The population density.
4 The two parts of the country where the population is most concentrated.
5 Three major natural resources.
6 The country’s ranking on the 2012 Human Development Index.
7 The net migration rate.
8 The contrast with the net migration rate of Bangladesh.
9 The infant mortality rate of Australia and Bangladesh.
10 The life expectancy of Australia and Bangladesh.
| canada_and_tanzania_case_studies.pdf | |
| File Size: | 3974 kb |
| File Type: | |
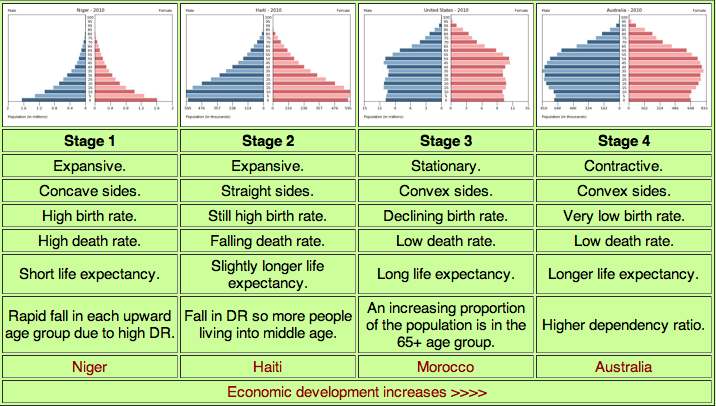
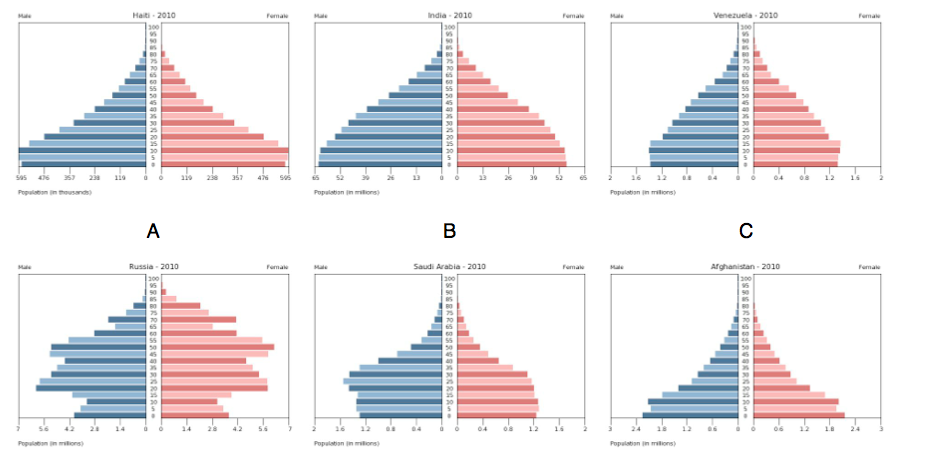
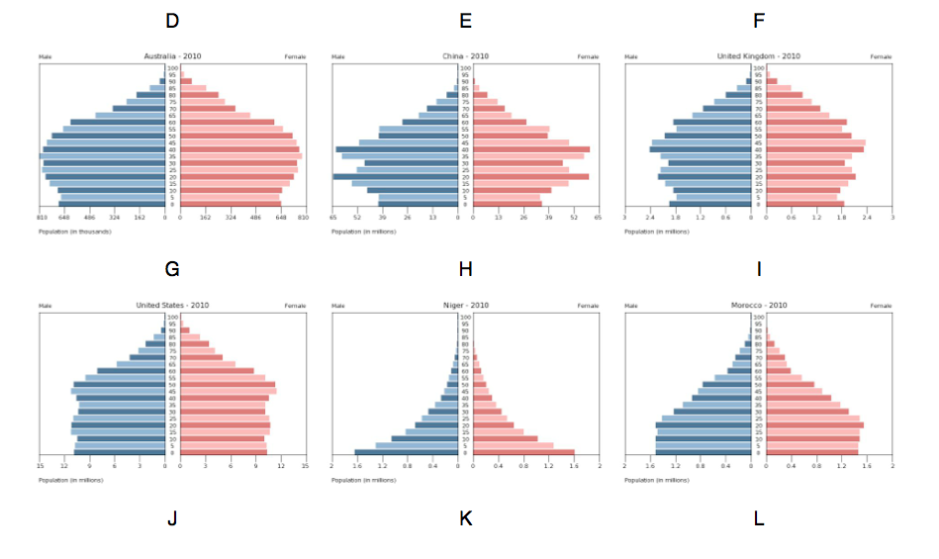
Population Pyramids
A population pyramid: also called an age pyramid or age picture diagram, is a graphical illustration that shows the distribution of various age groups in a population (typically that of a country or region of the world), which forms the shape of a pyramid when the population is growing
|
|
|
|
Complete the following worksheet and then decide which of the following Pyramids fit into which stage? Why is this the case?
| |||||||
| Sweden Case Study | |
| File Size: | 3741 kb |
| File Type: | |
Contrasting rates of population change
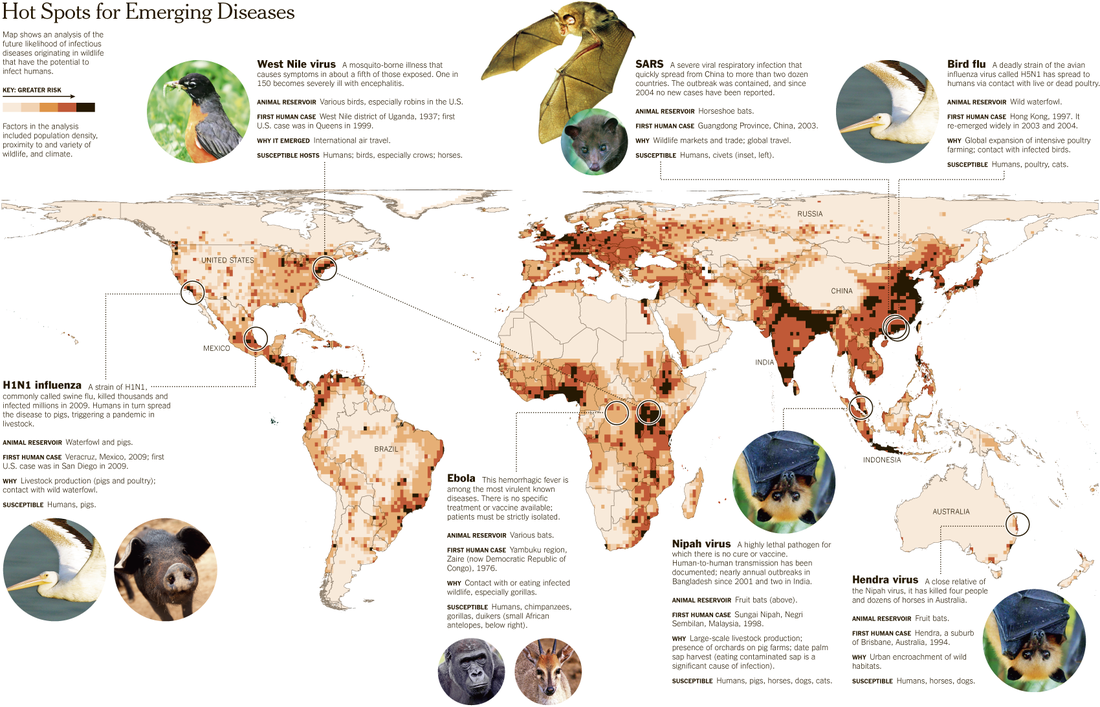
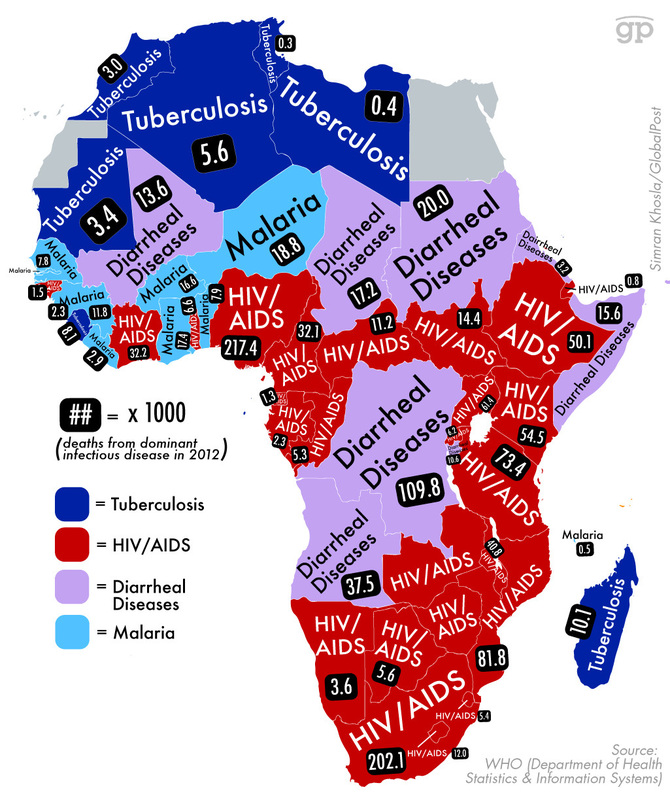
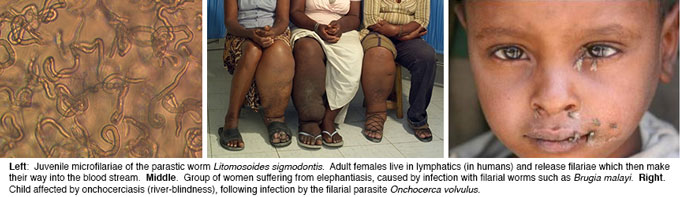
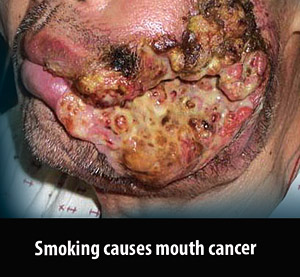
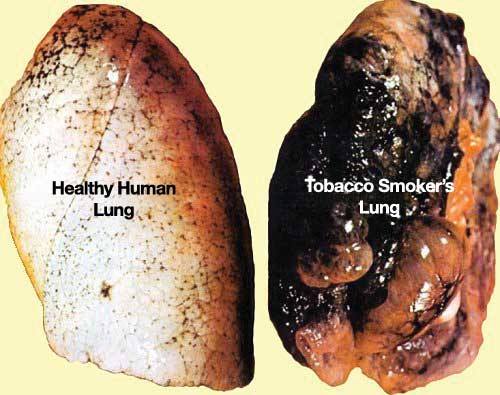
Diseases
|
|
|
|
Complete the following worksheet
| |||||||
Government Policies on population Control
Pro-Natalist & Anti-Natalist
|
Task:
You will be conducting a debate on which Government policies to control population work best. However, before you start you will have to research these policies. Create a brief overview of each policy- 2 documents (maximum 1 side of A4) Pro-natalist: France Anti-natalist: China
|
| ||||||||||||||||||