Please help keep the Geographer Online a FREE resource
Populations in transition
Index
Population Change
Key Terms
|
|

Complete the Introduction to Population change worksheet by using the YouTubes below.
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
Starter activity: Try to define the Key Terms using your own knowledge. Do they match the official definitions?
- The Glossary of Demographic Terms
- See the top of the page
| Population Key Terms | |
| File Size: | 26 kb |
| File Type: | doc |
Revise this PowePoint at home to remind yourself of about population
| Population Revision | |
| File Size: | 17214 kb |
| File Type: | ppt |
|
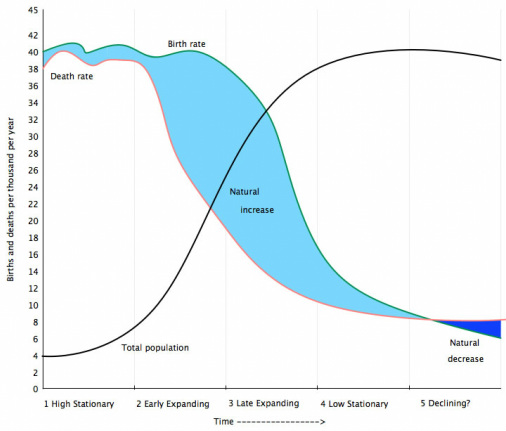
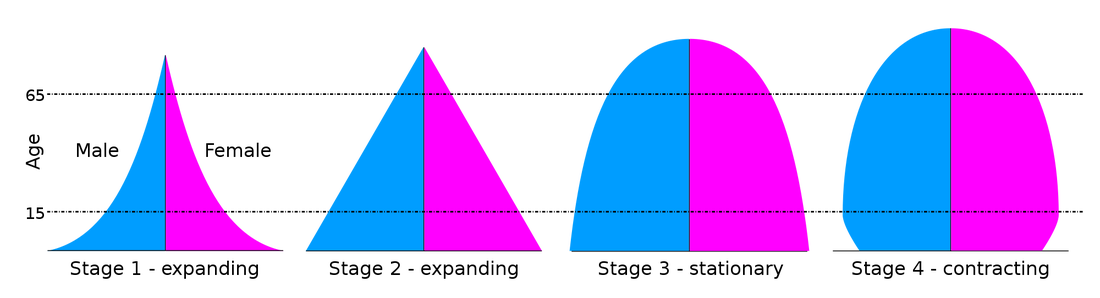
Explain and annotate the Demographic Transition Model (DTM). You can use this website and the following presentation |
| Demographic Transition Model | |
| File Size: | 557 kb |
| File Type: | ppt |
Diagram Questions:
Practising Description questions:
In Paper 1 of the IB examination it is very common to see 3 mark description based questions. These are very easy providing you ensure that you describe trends and also include correct data from the source. DO NOT just give examples from the data this is NOT describing and whatever you do do NOT start explaining or interpreting this data, it is not what is asked for.
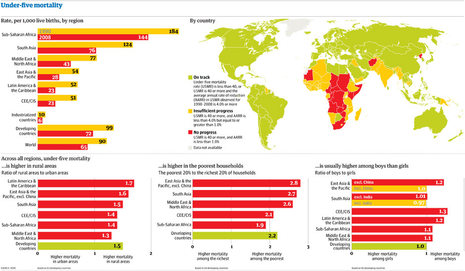
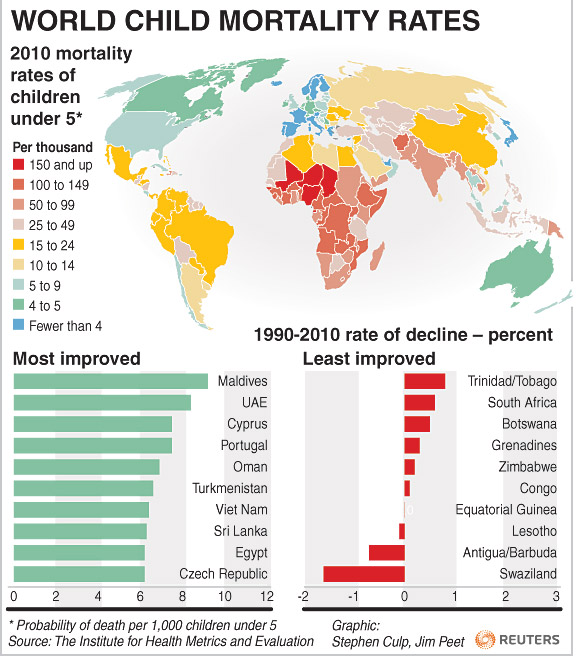
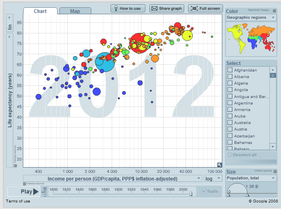
Using the interactive map below select any 3 criteria (excluding Child Mortality rate) and describe the global pattern [3 marks each]
In Paper 1 of the IB examination it is very common to see 3 mark description based questions. These are very easy providing you ensure that you describe trends and also include correct data from the source. DO NOT just give examples from the data this is NOT describing and whatever you do do NOT start explaining or interpreting this data, it is not what is asked for.
Using the interactive map below select any 3 criteria (excluding Child Mortality rate) and describe the global pattern [3 marks each]
Play the Gapminder game guess and justify some global population trends
|
Watch the Horizon documentary and answer the questions from the worksheet.
(worksheet courtesy of Geographypods)
|
| ||||||
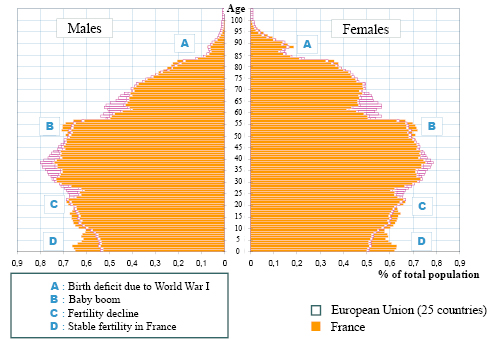
Population Pyramids
|
Revision YouTube on Population pyramids - Make notes on what is a population pyramid and what it shows.
|
| ||||||
Using the Population Pyramid Interactive Site describe and explain some example trends and anomalies (interpret these).
Population momentum and projections
Population momentum - Make notes on the YouTube. Answer the question: 'Outline ways we can halt the global population explosion'
Population momentum refers to population growth at the national level that would occur even if levels of childbearing immediately declined to replacement level.
Population momentum refers to population growth at the national level that would occur even if levels of childbearing immediately declined to replacement level.

IB Style Question: Distinguish between population projection and population momentum, explain the differences. [4]
Responses to High and Low Fertility
Make notes from the PowerPoint on ageing and youthful populations. Remember to pay special attention to the case studies.
| ageing_and_youthful_populations.pptx | |
| File Size: | 12681 kb |
| File Type: | pptx |
|
Dependency Ratios:
|
| ||||||
| aging_population_consequences_geofile.pdf | |
| File Size: | 37 kb |
| File Type: | |
|
The Causes of an ageing populations
High life expectancy caused by:
|
Problems of an ageing population
|
Solutions to an ageing population
|
Advantages of an ageing population
|
|
Advantages of elderly workers
|
Disadvantages of elderly workers
|
Pro-Natalist and Anti-Natalist policies - Case studies
| population_policies.pptx | |
| File Size: | 7273 kb |
| File Type: | pptx |
Project:
As part of the IB DP course you will need to study some examples of Pro Natalist and Anti Natalist policies. Divide up the the class into groups and each group will need to produce:
The webpage should:
As part of the IB DP course you will need to study some examples of Pro Natalist and Anti Natalist policies. Divide up the the class into groups and each group will need to produce:
- An information webpage - outlining examples and evaluating Pro/Anti natalist policies.
- A 3 minute (max) Youtube about your main case study. Include visual aids but do not mention your name, the school or show yourself.
The webpage should:
- Explain what are Pro/Anti Natalist policies
- Give some real life examples of these policies
- Provide a background of your main case study - China/France
- What is the actual policy, who does it apply to and are there any exceptions
- What are its successes/failures
- What about today? Has anything changed?
| Website Assessment Criteria | |
| File Size: | 15 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
To be able to complete these tasks you will need a lot of resources. Please go to the following pages to find some useful information:
Student Websites
These sites were made by previous students
These sites were made by previous students
Movement Responses - Migration
|
Define the key terms on migration:
|
You can find definitions here:
| ||||||

Study the website People on the Move and discuss some of the migration patterns present.
Watch the following YouTubes and describe the key movements of people around the world, why do you think these patterns occur? Make notes.
|
|
|
|
IB Style Questions:
Use the following to answer:
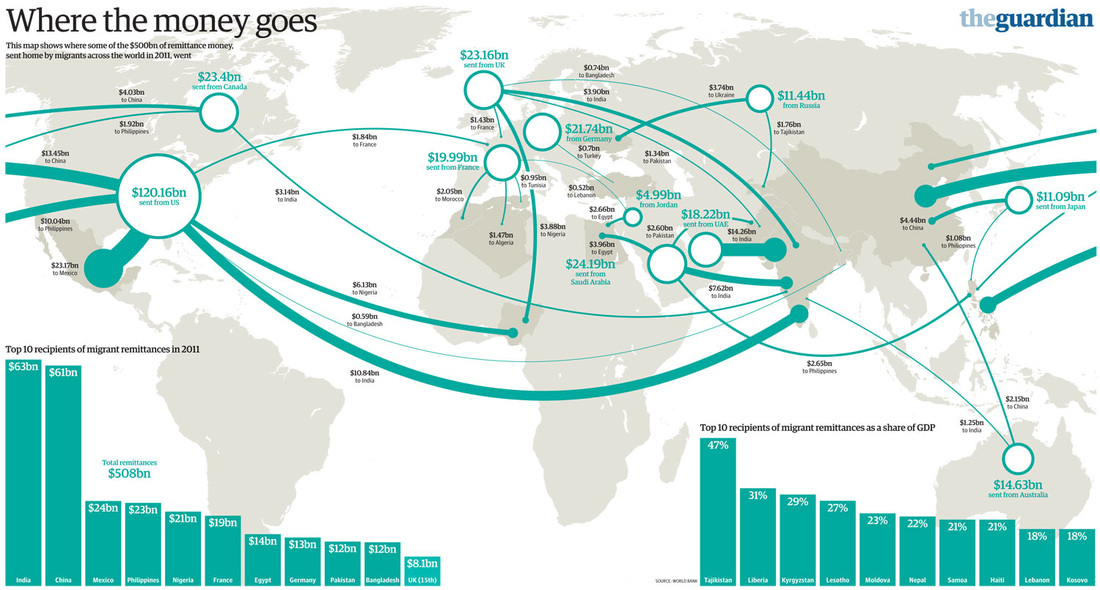
Russia’s rouble crisis poses threat to nine countries relying on remittances
- What are remittances and describe the global trend [5]
- Explain why remittances are useful for developing countries [5]
Use the following to answer:
Russia’s rouble crisis poses threat to nine countries relying on remittances
A Basic Overview of Why People Migrate:
People migrate for many different reasons. These reasons can be classified as economic, social, political or environmental:
A refugee is someone who has left their home and does not have a new home to go to. Often refugees do not carry many possessions with them and do not have a clear idea of where they may finally settle.
People migrate for many different reasons. These reasons can be classified as economic, social, political or environmental:
- economic migration - moving to find work or follow a particular career path
- social migration - moving somewhere for a better quality of life or to be closer to family or friends
- political migration - moving to escape political persecution or war
- environmental causes of migration include natural disasters such as flooding
A refugee is someone who has left their home and does not have a new home to go to. Often refugees do not carry many possessions with them and do not have a clear idea of where they may finally settle.
|
Push factors are the reasons why people leave an area. They include:
|
Pull factors are the reasons why people move to a particular area. They include:
|

Task:
You will need to know some of the migration models for your IB course. There are 6 of them and you need to investigate and create some notes on each. Use the two files below to help you.
|
| ||||||||||||
Case Studies:
You will need case studies to discuss (both on internal migration and external migration). Ensure that you are also making notes on the positive and negative effects on the country of origin and the host country.
You will need case studies to discuss (both on internal migration and external migration). Ensure that you are also making notes on the positive and negative effects on the country of origin and the host country.
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Migration from Steven Heath
| migration_2008.pptx | |
| File Size: | 1224 kb |
| File Type: | pptx |
|
Online Activity Plenary activities:
You are an Immigration officer explore various Case Studies and decide whether you would offer them a Visa BBC Website. |
Refugee simulation and interactive site
|

So .... Is migration bad? What do you think?
Gender and Change
|
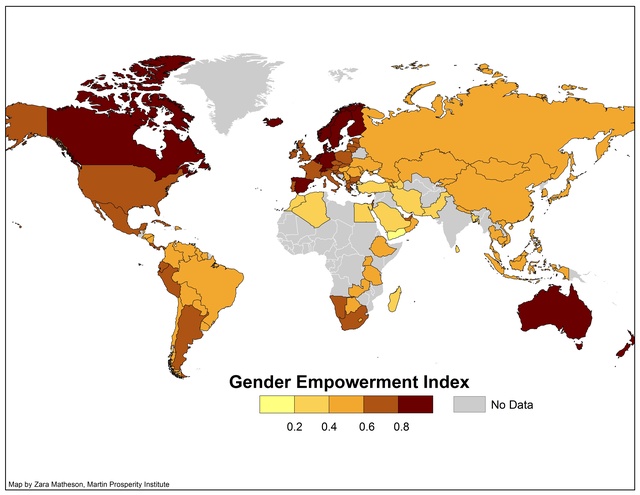
What is Gender Equality?
|
Some useful links
|

Kenya project:
As part of the planned Kenya visit you could become more involved in promoting and aiding gender equality in Kenya. There are many ways you can get involved in this, for example: The BOMA project
|
Culture and Status
Make notes on the most extreme cases of gender inequality. Remember to give examples. Interesting informatic on the gender gap in Hollywood |
|
Education
|
Why is female education important
|
What Problems can a lack of Education Cause?
|
|
Additional Sources:
|
|
IB Style Question:
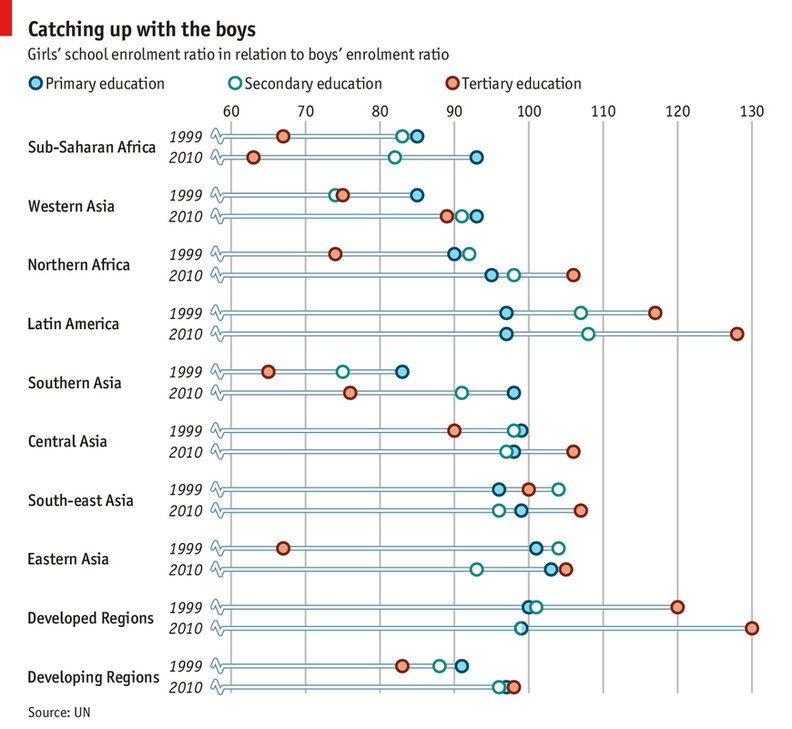
Using the graph below describe the changes that have occurred in the education of girls between 1999 and 2000.
Using the graph below describe the changes that have occurred in the education of girls between 1999 and 2000.

IB Style Question: Essay - Plan this essay essay and write it as a group. Work together to create the ideal essay.
To what extend do women experience inequalities in health treatment? Discuss. [15]
To what extend do women experience inequalities in health treatment? Discuss. [15]
| gender_and_hivaids.pdf | |
| File Size: | 607 kb |
| File Type: | |
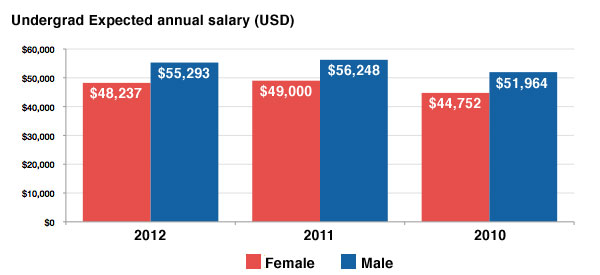
Employment, Empowerment and Legal Rights
Class activity - Using the presentation outline below fill in the relevant pages with the sourced information that follows. Everything is in order.
| gender_inequalities_template_for_class_activity.pptx | |
| File Size: | 53 kb |
| File Type: | pptx |
Resources for Class Activity
|
Property Rights
Honour Killings Driving |
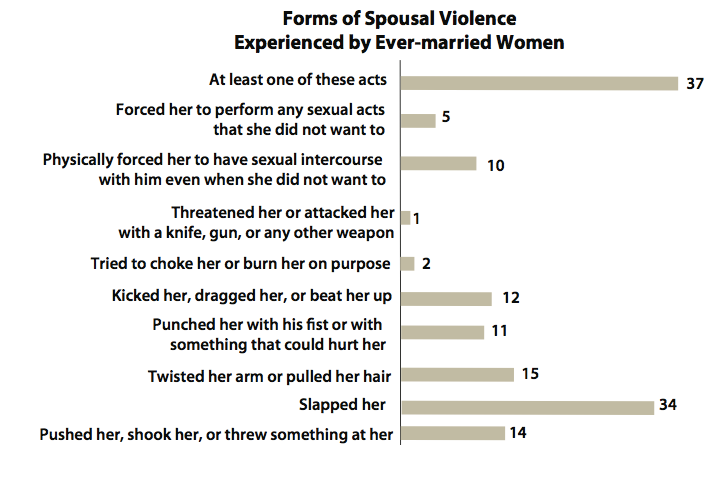
Violence
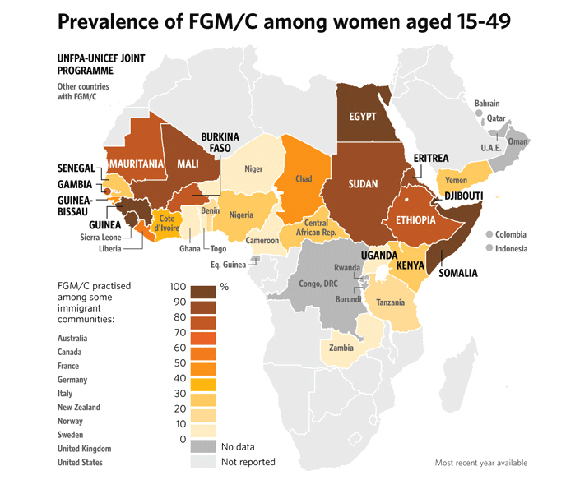
Female Genital Mutilation (FGM)
|
The Girl Effect
Explain what the Girl Effect is and why it is important for Gender equality
Explain what the Girl Effect is and why it is important for Gender equality
|
|
|
|
What is standing in the way of Gender Equality
Revision Notes

These notes have not been written by me and as such are only to help give you ideas about revision NOT to be used as your main source of revision. That should be your own notes!
| ib_geog_hl_populations_in_transitionrevision_notes_2012.pdf | |
| File Size: | 1001 kb |
| File Type: | |