Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| water.pdf | |
| File Size: | 113 kb |
| File Type: | |
The earths water supply
Key Words
- Water Surplus: There is more fresh usable water that is needed for the needs of the area (population and activities).
- Water Deficit: There is not enough fresh usable water to meed the needs of the area
|
In this Unit we will be examining the Fresh Water Supply.
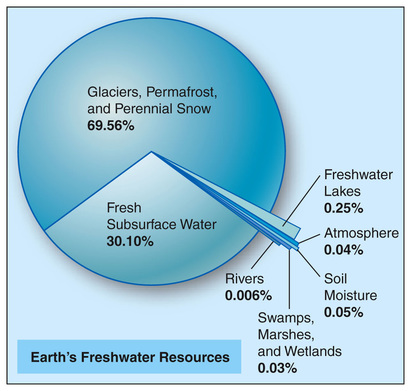
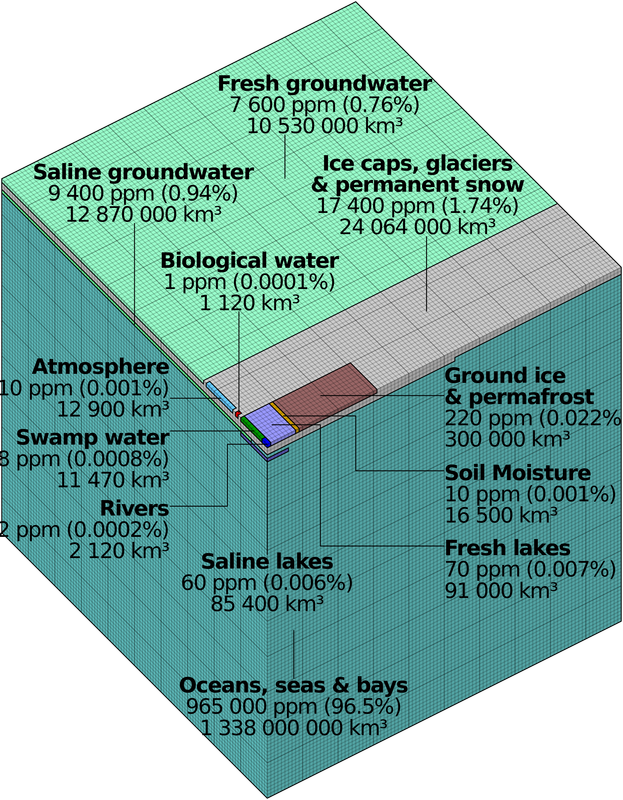
Using the graphs to examine where the Earth's water supply is found and determine what percentage is usable for People and Agriculture and where it comes from.
|
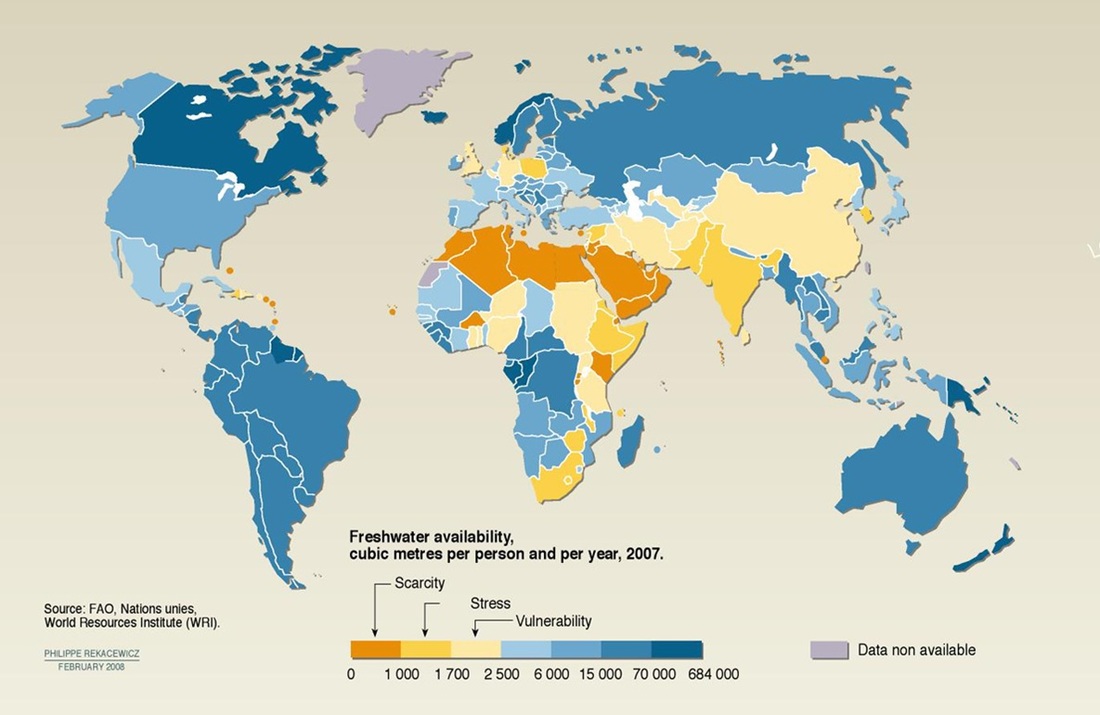
Whole class discus the factors that affect water shortages (create a mind map) • supply (e.g. precipitation, temperature, evaporation rates, rivers, pollution and infrastructure, etc.) and • demand (e.g. economic activities, population distribution and country’s level of development, etc.) |
|
|
|
|
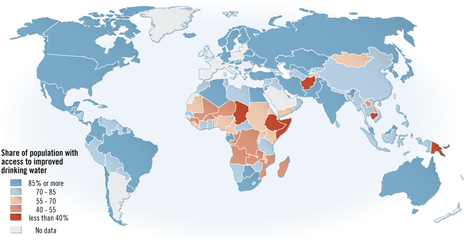
Access and Demand for water
Group Project:
Create a presentation (use microsoft SWAY) explaining the following areas.
Create a presentation (use microsoft SWAY) explaining the following areas.
- What factors influence how much water an area has?
- What is water demanded for? (use examples of quantity)
- Where do we get our water from? (give as many sources as possible & briefly explain them)
- What is being done to improve water supply for the poor and vulnerable - give examples.
- Water facts from around the world
Sources of information
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| Water Scarcity or Surplus? | |
| File Size: | 1981 kb |
| File Type: | |

Extended writing activity: Why do water shortages occur in some parts of the world and not others?
Water Supply & Conservation
Supply Method |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
River, lakes and other natural bodies of water |
Water is naturally available and it is easy to access it and distribute it to users. Dams and reservoirs can be build to further increase water storage. |
In LEDCs these sources can become easily polluted and if water is not treated it can carry diseases such as cholera. |
Wells and bore holes |
Water is naturally purified by filtration through bedrock and can exist in arid areas where there is limited surface water eg. Great Artesian Basin in Australia |
Constructing wells costs money as does extracting the water through pumps. It is usually limited in quantity and can not sustain large populations or agriculture. |
Desalinisation plants |
Supply is virtually unlimited (sea water) |
It is extremely expensive and uses a lot of energy (Global Warming) |
Rainwater harvesting |
Water is usually very pure and can be consumed with limited treatment |
Rain is unpredictable and storage of water can be difficult. |
Water condensing |
Water is very pure and does not require any treatment. Technology is inexpensive and simple. |
Can only provide small quantities of water. |
Appropriate technology: technology that is suitable to the social and economic conditions of the geographic area in which it is to be applied, is environmentally sound, and promotes self-sufficiency on the part of those using it.
|
|
|
Case Study
Water supply in Lesotho and South Western USA:
The water problem in south-western USA
State:
- Locate the area using a map and describe the location.
- Outline the distribution of water sources (include place names)
- Discuss issues of water management (what is being done?)
- How is this likely to affect the future of the country?
The water problem in south-western USA
State:
- The percentage land area, population and precipitation of the USA in the western states.
- The year of the Reclamation Act.
- The area of irrigated land in California.
- Two areas of irrigated farmland in the state.
- The percentage of California’s water used by agriculture.
- The population depending on the Colorado river for water.
- A major dam on the Colorado river.
- The last major scheme diverting water from the Colorado river.
- The main cities bene ting from this water.
- Two resource management strategies to improve the water supply situation.
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| case_study_usa.pdf | |
| File Size: | 5329 kb |
| File Type: | |
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| water_source_case_study.pdf | |
| File Size: | 3849 kb |
| File Type: | |