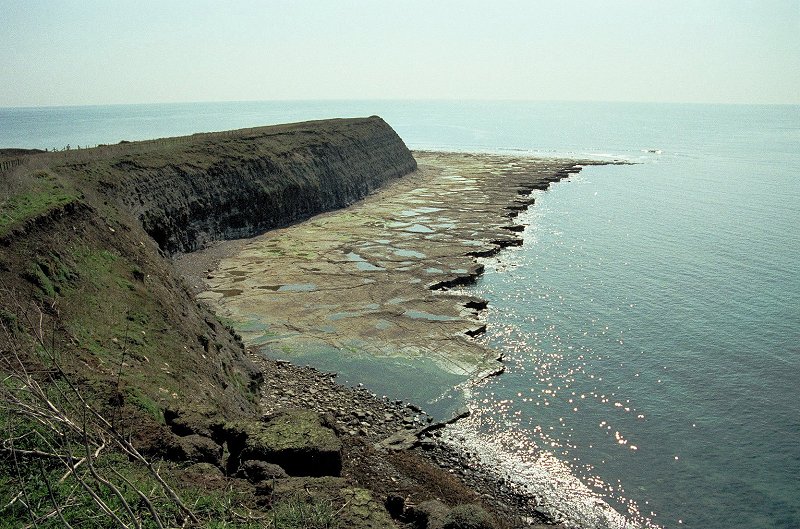
Lesson 1: What are coasts and why are they so important?
|
Print and complete the worksheet explaining what coasts are and their different parts.
| |||||||
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Create a 1 page information fact-sheet illustrating why coasts are useful. Your fact-sheet should contain.
- Explanation of what coasts are.
- Diagrams and images of coasts.
- Interesting numerical facts about coasts.
- A list of human and physical uses of coasts.
Lesson 2: Different types of coasts and waves
|
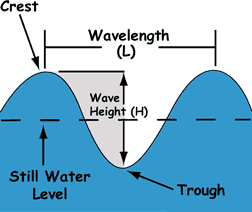
Draw a labelled diagram of waves and define all the key terms. Complete the worksheet below.
| |||||||||
- Crest: The top of the wave.
- Trough: The low area in between two waves.
- Wavelength: The distance between two crests or two troughs.
- Wave height: The distance between the crest and the trough.
- Wave Frequency: The number of waves per minute.
- Velocity: The speed that a wave is traveling. It is influenced by the wind, fetch and depth of water.
- Swash: The movement of water and load up the beach.
- Backwash: The movement of water and load back down the beach.
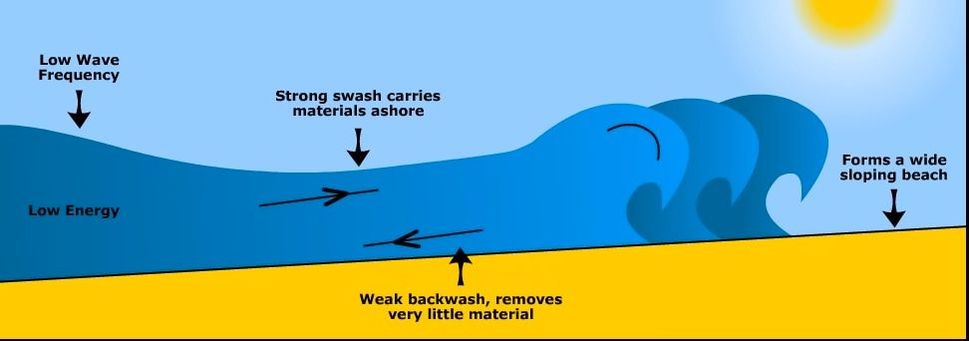
Draw and explain the following two types of wave.
|
Review the unit and key words - close books and use mini whiteboards to answer revision questions
|
Lesson 3: Coastal processes:
erosion, transportation & deposition
Coastal erosion
The sea shapes the coastal landscape. Coastal erosion is the wearing away and breaking up of rock along the coast. Destructive waves erode the coastline in a number of ways:
The sea shapes the coastal landscape. Coastal erosion is the wearing away and breaking up of rock along the coast. Destructive waves erode the coastline in a number of ways:
- Abrasion or Corrasion
- Hydraulic Action
- Attrition
- Solution of Corrosion
| Coastal Erosion Worksheet | |
| File Size: | 41 kb |
| File Type: | doc |
|
Play the following Revision Kahoot
|
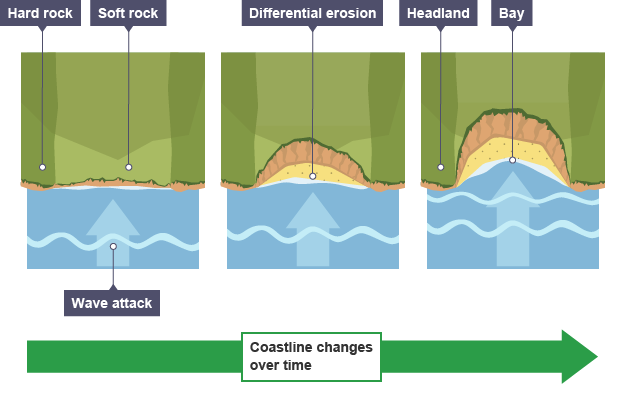
Lesson 4: Erosional Coastal features
|
Complete the erosional features worksheet. You will need to draw a diagram and also complete the explanation. To help you with the explanation divide up the diagram into logical stages - number them and then you will be able to create a brief sentence for each.
| |||||||
|
|
|
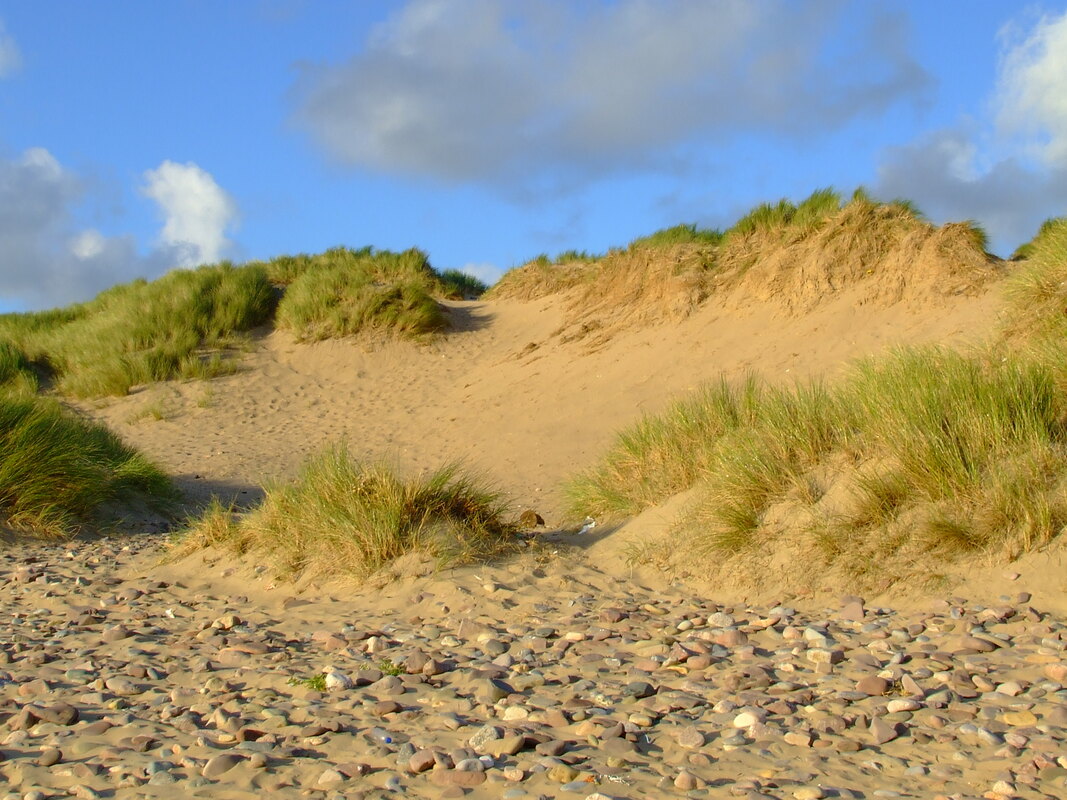
Lesson 5: Depositional Coastal features
|
Complete the worksheet on Depositional coastal features
| |||||||
|
Sand dunes from Steven Heath |
|
Coastal Features Revision Quizizz
|
Lesson 6: Coastal Defences
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| how_can_we_protect_the_coast_powerpoint.ppt | |
| File Size: | 10357 kb |
| File Type: | ppt |
Worksheets
|
| ||||||||||||
Information Sheets
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Lesson 7&8: Case STudy -Coastal Management
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| holderness_coast.ppt | |
| File Size: | 17938 kb |
| File Type: | ppt |
Worksheets and information sheets for group investigation/case study
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||