Please help keep the Geographer Online a FREE resource
Environmental Change
Index
|
|
|
Degradation through raw material production
Key Terms
|
|
Characteristics of
|
Regions where Agro-industrialisation is evident
|
|
|
|
|
Post by Animal Equality.

Case Study:
Examine the environmental consequences of increasing international demand on Soybeans. Use the Global Interactions text book pg 99.
Examine the environmental consequences of increasing international demand on Soybeans. Use the Global Interactions text book pg 99.
food Miles
Other Perspectives
|
|
|
|
|
|
The effects of transnational manufacturing and services
Key Terms
|
|
|
Read the document on the right and create a mind map showing all the factors that affect how TNCs locate around the world.
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|

Case Studies:
Watch the above YouTubes and make notes on where and why certain industries are located in countries outside the traditional core areas of Europe and North America.
Other supporting evidence:
Watch the above YouTubes and make notes on where and why certain industries are located in countries outside the traditional core areas of Europe and North America.
Other supporting evidence:
| mumbai-choking-e-waste_report_mail.pdf | |
| File Size: | 2183 kb |
| File Type: | |
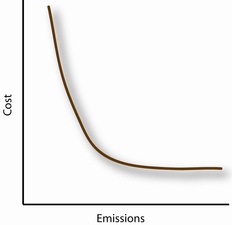
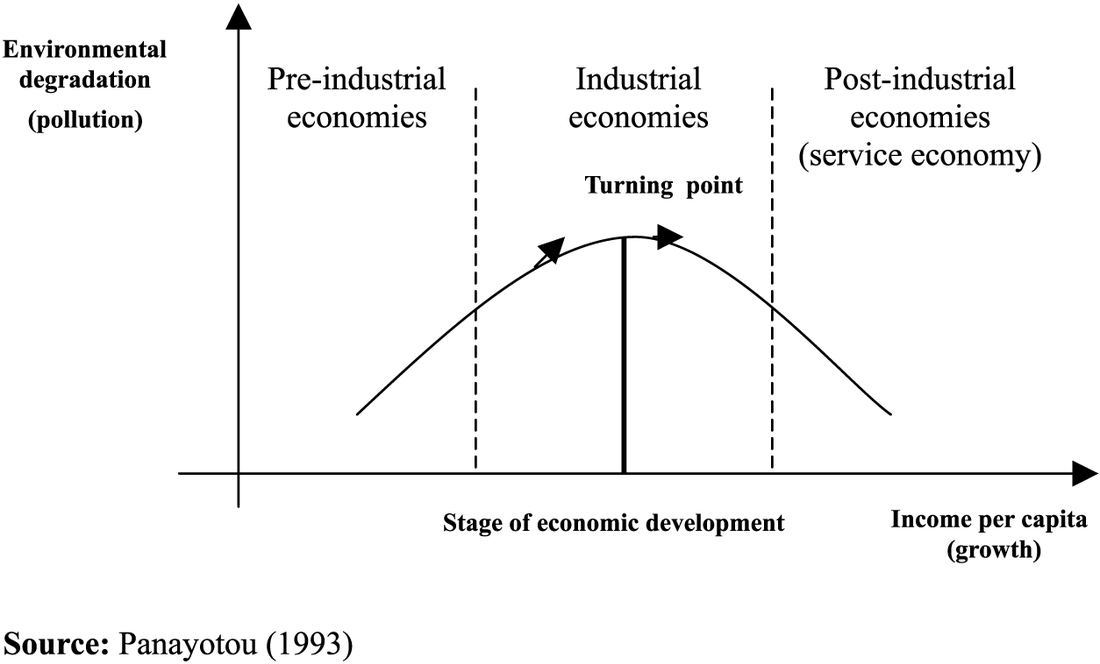
Draw and explain the following graphs:
|
|
|
TRANS BOUNDARY POLLUTION
Key Terms
|
|

This unit can be linked to:
- Optional Unit: Oceans and their Coastal Margins (Pacific Garbage Gyre)
- Optional Unit: Hazards and Disasters - Risk Assessment and Response (Chernobyl)
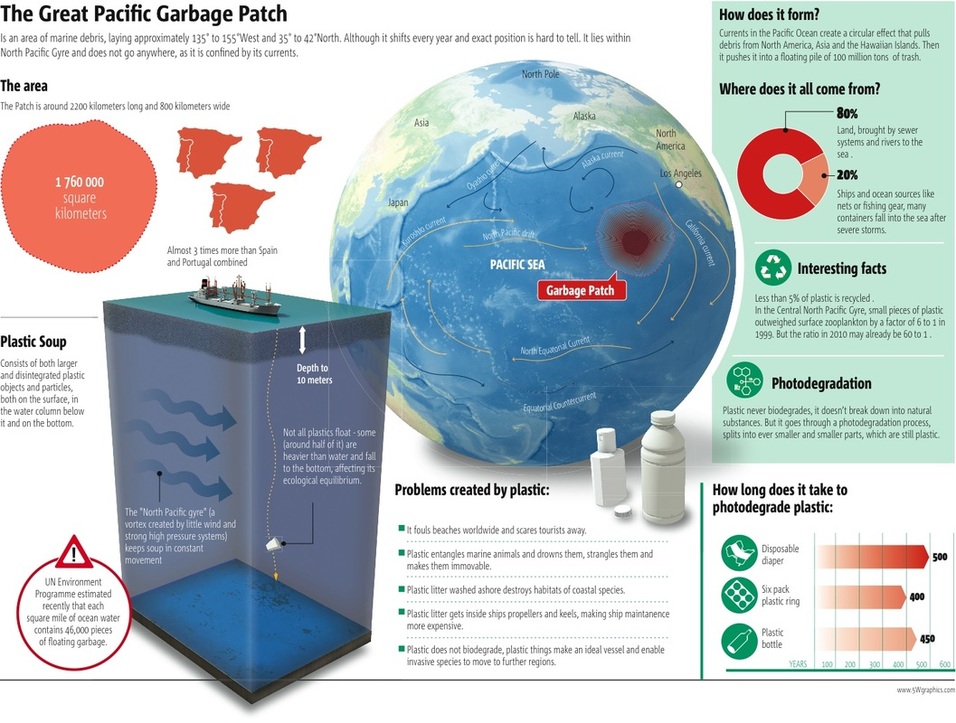
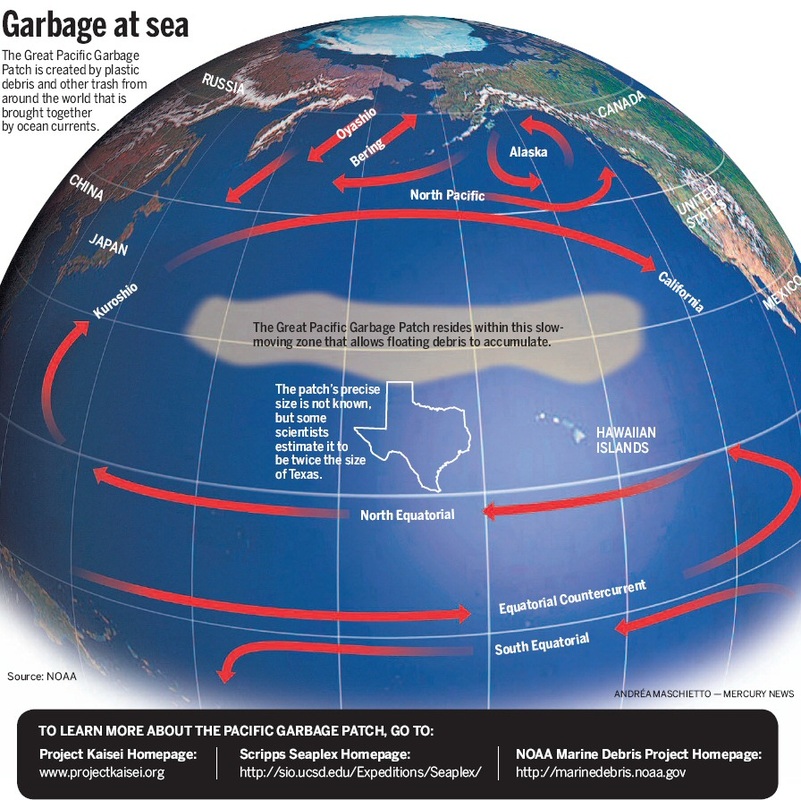
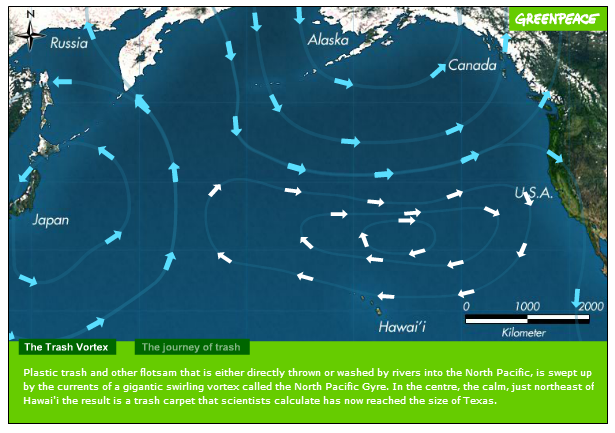
The Pacific Garbage Gyre
Classwork:
Go through all the images, pictures and videos whilst making some notes on each subheading areas.
Go through all the images, pictures and videos whilst making some notes on each subheading areas.
Where?
Causes?
Consequences?
Responses?

|
|
|
Greenpeace is an independent global campaigning organisation that acts to change attitudes and behaviour, to protect and conserve the environment and to promote peace by:
To maintain its independence, Greenpeace does not accept donations from governments or corporations but relies on contributions from individual supporters and foundation grants.
- Catalysing an energy revolution to address the number one threat facing our planet: climate change.
- Defending our oceans by challenging wasteful and destructive fishing, and creating a global network of marine reserves.
- Protecting the world's ancient forests and the animals, plants and people that depend on them.
- Working for disarmament and peace by tackling the causes of conflict and calling for the elimination of all nuclear weapons.
- Creating a toxic free future with safer alternatives to hazardous chemicals in today's products and manufacturing.
- Campaigning for sustainable agriculture by rejecting genetically engineered organisms, protecting biodiversity and encouraging socially responsible farming.
To maintain its independence, Greenpeace does not accept donations from governments or corporations but relies on contributions from individual supporters and foundation grants.
| GreenPeace Summary Sheet | |
| File Size: | 30 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
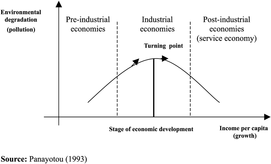
Reasons for Increased Social Awareness:
As suggested by the Kuznets curve, environmental awareness increases with economic development.
As suggested by the Kuznets curve, environmental awareness increases with economic development.
- Increased publicity and campaigning by NGOs and charitable organisations e.g. Greenpeace
- Increased coverage of environmental problems by media organisations e.g. BBC and CNN
- Environmental disasters like the BP Oil Spill have heightened awareness
- Improved economic development allows people to consider other matters rather than just the economy and making money
- Because people have more leisure time and greater disposable income they have more time to enjoy the environment so would like it protected
- Government have created more protected areas e.g. National Parks as well as the UN e.g. World Heritage Sites which has increased the profile of the environment
- Political parties like the Green party in the UK are growing in importance and stature and are increasing people awareness
- Environmental campaigns can be spread easily via social media like Youtube, Twitter and blogs
- Education about the environment e.g. the three R (reduce, reuse, recycle) has improved at school
- The number of recycling centres and recycling bins have increased which has increased awareness
- Environmental labelling e.g. FSC and Dolphin Friendly have made consumers more aware of the environment
- The environment has been made one of the Millennium Development Goals - Goal 7 is Environmental Sustainability
- UN conferences like the Rio Earth Summit have increased global awareness of the environment
- Global issues like acid rain, the greenhouse effect and the hole in the ozone layer are better understood and better publicised and taught
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
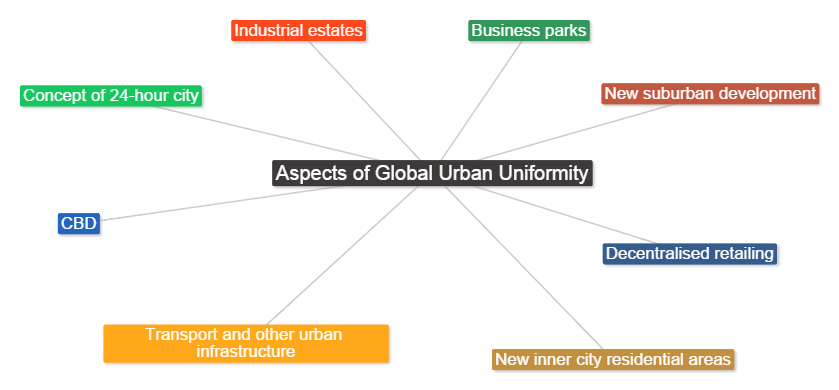
HOMOGENIZATION of Landscapes
Key Terms
|
|
Where are these places?
| Where are these places in the world? | |
| File Size: | 4040 kb |
| File Type: | pptx |

Using pages 132 - 138 in the Geography "Global Interactions" textbook answer the following questions:
IB Style Question:
Explain how urban landscapes have become more uniform in recent decades? [10]
- What common characteristics would you expect to find in the CBDs of large cities all around the world?
- What are the reasons for such similarities?
- Describe and explain other characteristics of urban areas which have become more uniform in recent decades.
- Explain the meaning of a 'gradient of homogenisation'
IB Style Question:
Explain how urban landscapes have become more uniform in recent decades? [10]