Please help keep the Geographer Online a FREE resource
Settlements
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| settlements.pdf | |
| File Size: | 139 kb |
| File Type: | |
Site & Situation
Key Terms
|
|
You will watch this YouTube once and then in groups you will try to summarise the key ideas in 1 minute. So, pay attention, make notes and prepare to explain what you have learnt.
|
Using the YouTube and the information on the SCool Website complete the following worksheet.
|
| |||||||
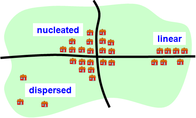
Patterns
|
Use the presentation below and make notes on the three different types of settlement pattern you can see. Then use the maps and satellite images to practice spotting them.
|
| ||||||
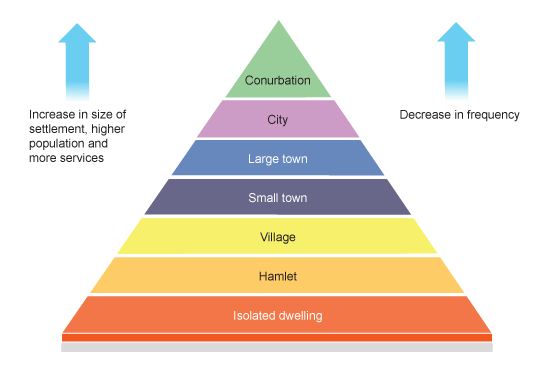
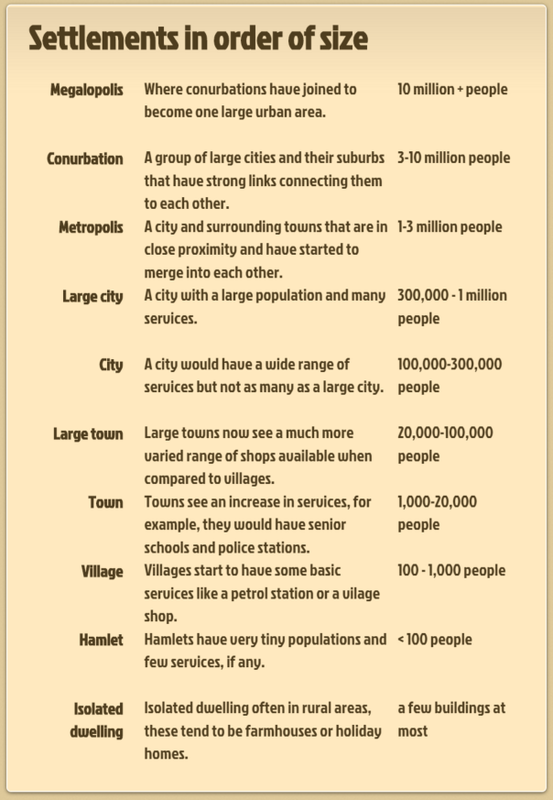
Settlement Hierarchy
Key Terms
|
|
|
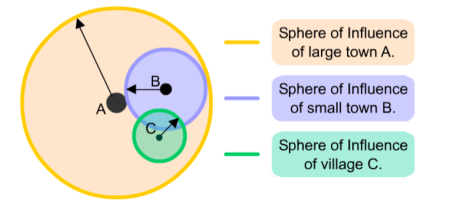
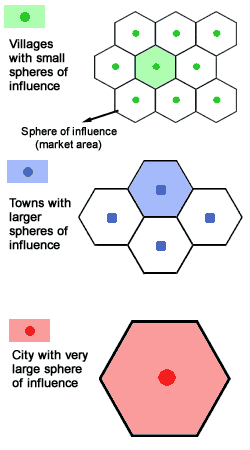
Larger settlements and conurbations have a much larger sphere of influence than smaller ones. This means they attract people from a wider area because of the facilities they offer. Cities such as London have a global sphere of influence, whereas a small hamlet or village may only have a sphere of influence of a couple of kilometres.
Amount of people living in a settlement is not always a good way of determining the hierarchy of a settlement. Sometimes, the types of services that are found in a settlement can determine its hierarchy — from essential services like schools and hospitals to entertainment and leisure services such as online casinos. Click on the link to examine the following services. |
Diagram from: 3DGeography
|

Create a list of Low and High Order goods. Then examine what type of services each settlement type has.
|
Central Place Theory:
This is related to the sphere of influence any settlement has. If you look at the diagrams you can see that a village will have a small sphere of influence and a city will have a large sphere of influence. Theoretically the services that are found in a city such as an international airport, government offices, etc need a threshold population to sustain them and so you can not have two cities inside the same sphere of influence. However, smaller settlements such as towns and villages only have services that require a smaller threshold population and therefore can be found in the sphere of influence of a city. |
|
Case Study:
Population size and number of services in Lozère Page 40-41 Locate Lozere on a map State: 1 In which country Lozère is situated. 2 The largest settlement in Lozère. 3 The population of the largest settlement in Lozère. 4 When Lozère’s population reached a maximum. 5 Settlements that have a rail link. 6 Settlements that offer skiing. 7 Settlements that have the smallest range of services. 8 The distance someone from Mende must travel to go skiing. 9 The highest settlement in the region. 10 The name of the settlement which has a full range of services. orCase Study:
Isle of Wight Answer the questions on the PDF and the following questions.
|
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| Isle of Wight | |
| File Size: | 3452 kb |
| File Type: | |