Please help keep the Geographer Online a FREE resource
Urban Settlements
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| urban_settlements.pdf | |
| File Size: | 129 kb |
| File Type: | |
Urban land use models
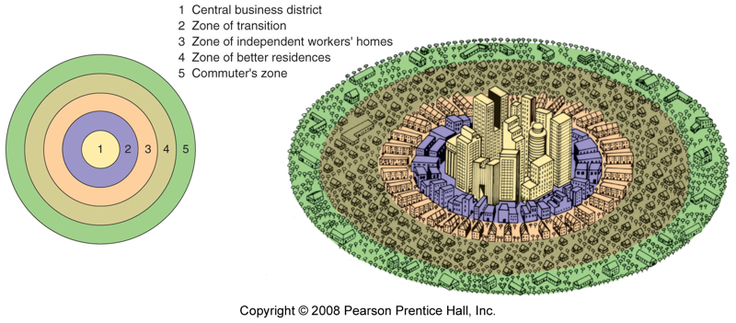
Burgess - Concentric Model
Burgess concluded that city land-use could be identified as a series of concentric rings around the CBD. The CBD will contain all the major shops and offices and be a centre of entertainment. Surrounding this CBD will be the oldest housing, which is in a state of deterioration. Industry will also feature in this area. This is the area often referred to as the inner city or 'zone of transition'. Then, we get three rings of housing. The first will be high density, poor quality that traditionally houses the workers for the factories. Next, is slightly lower density, middle class housing. These will be semi-detached with gardens. Finally, there is a ring of high class housing for those who can afford to commute.

Complete the Burgess land use worksheet by using the YouTube below and discussing the zones in class.
|
| ||||||||||||
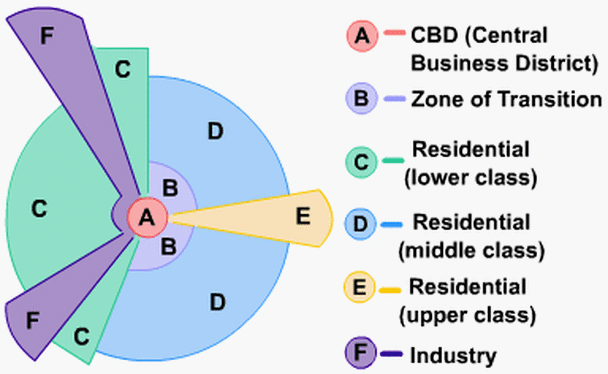
Hoyt Urban Model
Hoyt suggested that the city grew in a series of sectors or 'wedges'. These would grow along traditional communication routes. The land-use within a sector would remain the same as like attracts like. For example, a 'high class' sector would remain high class as it would be the most desirable area to live, so only the wealthiest could afford it. An industrial sector would remain industrial as the zone would have a common advantage - perhaps a railway line or river.
Note how the low quality housing is next to the industrial zone, middle class next to low class and high class as far as possible from industry and low class.
Note how the low quality housing is next to the industrial zone, middle class next to low class and high class as far as possible from industry and low class.

Complete the Hoyt land use worksheet by using the YouTube below and discussing the zones in class
|
| ||||||
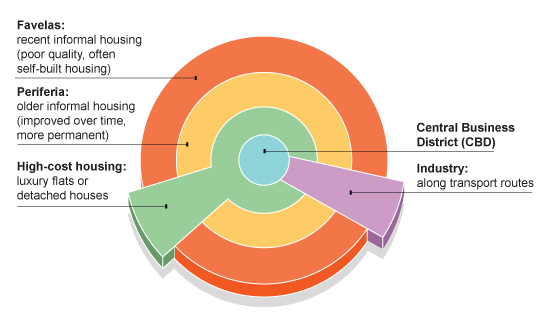
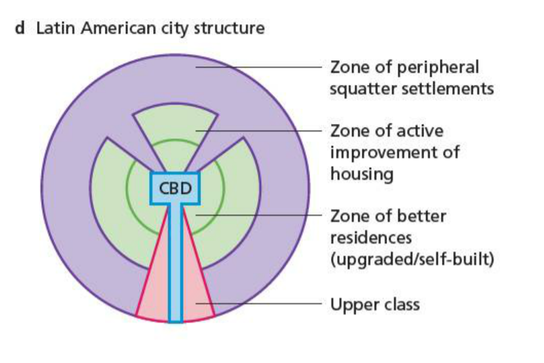
Urban Model for a developing country
The CBD is similar to that in the developed world and is an area of high-rise offices and shops. However, the similarities stop here. The CBD is surrounded by high-class apartments and older middle class housing, which has been built during colonial times.
You should not forget that there is great wealth in the cities of the developing world and that one of the features of the developing world cities is the great contrast in living standards.
In a ring around the high class housing you find well established 'shanty towns'. These will be the oldest shanty towns in the city and are located here so that residents could find work in the CBD or in the homes of the higher-class residents.
These are not like the shanty towns in the outer circle as they have been steadily improved by the residents. Many will have electricity, water supplies, even schools and clinics. The buildings will have been improved so that corrugated iron is replaced with brick and concrete. This could have been via a redevelopment scheme as outlined in the problems and solutions scheme. Many will now be officially recognised settlements.
This zone is referred to as 'periferia' or periphery.
Surrounding this (and infilling any gaps) will be the shanty towns that would be resident to the most recent migrants and would typically have the poorest standards of living as outlined in the urban problems section.
In addition, there are sectors of industrial use (as factories locate along main roads especially those that lead directly to a port) and residential as the high classes choose to leave the polluted and over-crowded inner city.
You should not forget that there is great wealth in the cities of the developing world and that one of the features of the developing world cities is the great contrast in living standards.
In a ring around the high class housing you find well established 'shanty towns'. These will be the oldest shanty towns in the city and are located here so that residents could find work in the CBD or in the homes of the higher-class residents.
These are not like the shanty towns in the outer circle as they have been steadily improved by the residents. Many will have electricity, water supplies, even schools and clinics. The buildings will have been improved so that corrugated iron is replaced with brick and concrete. This could have been via a redevelopment scheme as outlined in the problems and solutions scheme. Many will now be officially recognised settlements.
This zone is referred to as 'periferia' or periphery.
Surrounding this (and infilling any gaps) will be the shanty towns that would be resident to the most recent migrants and would typically have the poorest standards of living as outlined in the urban problems section.
In addition, there are sectors of industrial use (as factories locate along main roads especially those that lead directly to a port) and residential as the high classes choose to leave the polluted and over-crowded inner city.
Follow the following link and discuss which model you think this matches and why

Complete the City zone worksheet |
| ||||||

Print out:
Discuss the above model. How would this impact what the city looks like?
Discuss the above model. How would this impact what the city looks like?
Urban Problems

Using Coggle and after watching the YouTube create a spider diagram of the problems that cities can experience. Try to divide them into areas:
|
|

As a group discuss the possible solutions and add these to your coggle
London
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| london.pdf | |
| File Size: | 1560 kb |
| File Type: | |
|
|
|
|
Essay
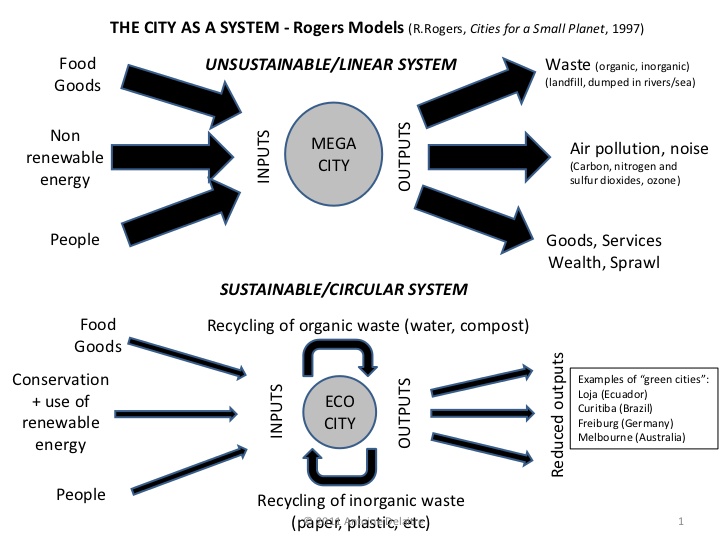
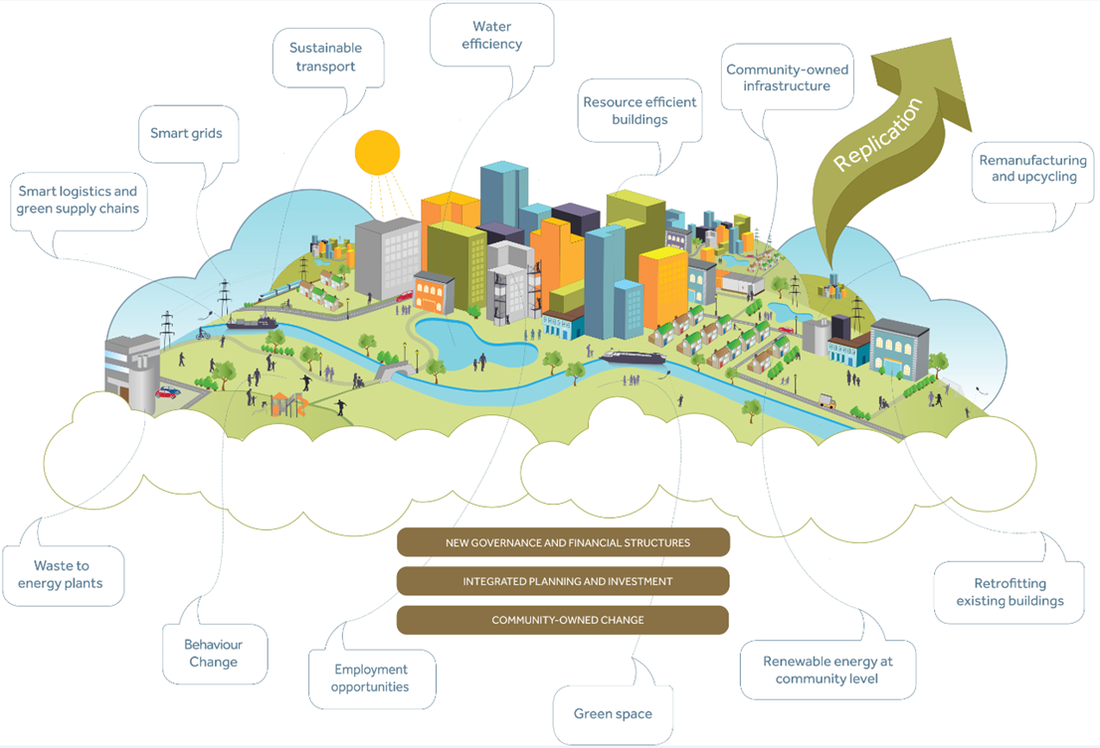
"Can cities be sustainable? Discuss"