Please help keep the Geographer Online a FREE resource
Changing space - the shrinking world
Index
Time Space Convergence
Key Terms
|
|
Make notes on the YouTube on Globalization. Which devices made the world smaller, how did they do this and what impact have they had on the world?
|
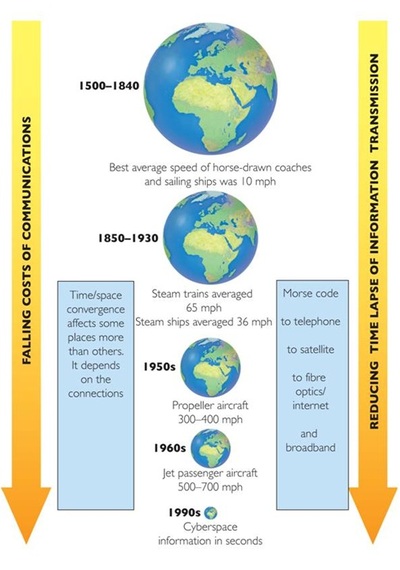
What is Time-space convergence?
The process, made possible by technological innovations in transportation and communication, by which distant places are brought closer together in terms of the time taken to travel (or send messages) between them. |
|
A MUST read - Transportation and Space
Essay: Explain what factors influence the Time-Space convergence? Note: [10 mark] essays ONLY in Global Interactions do not require evaluation. |
Print the following document to help explain how Sea and Air travel have impacted the world and what are the advantages and disadvantages of each.
| Advantages - Disadvantages of Sea/Air Travel | |
| File Size: | 23 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
|
|
|
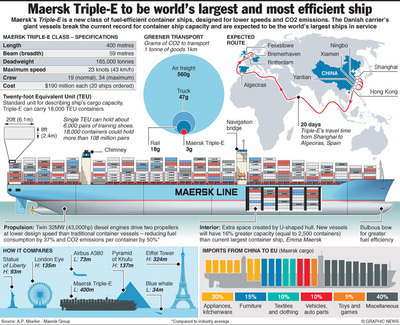
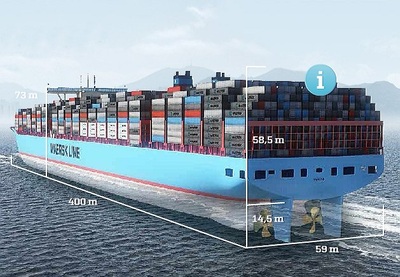
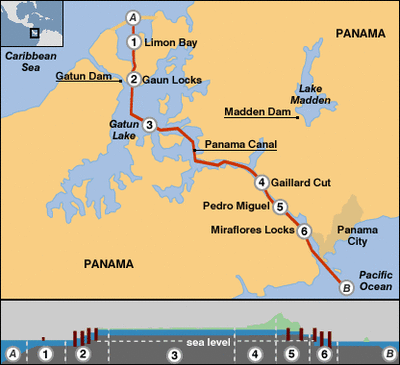
Sea Travel - Containerization
|
View and discuss this BBC article on historical shipping
|
What is Containerization and what impact has it had on the world and Globalization? Watch the YouTube below.
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
|
|
|
Air Travel
|
|
Watch the YouTube on the left and consider. Where are the largest concentrations of flights and when do they occur?
|
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
|
How the air industry has changed - Images from the Telegraph Airline History
|
|
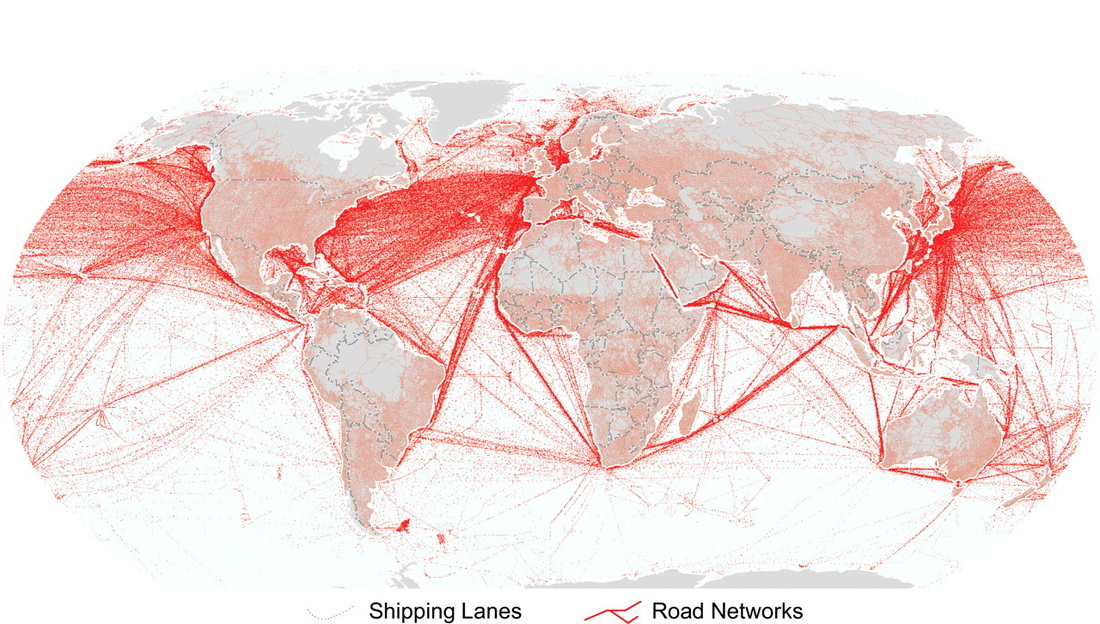
Extensions and Density of Networks
Key Terms
|
|
|
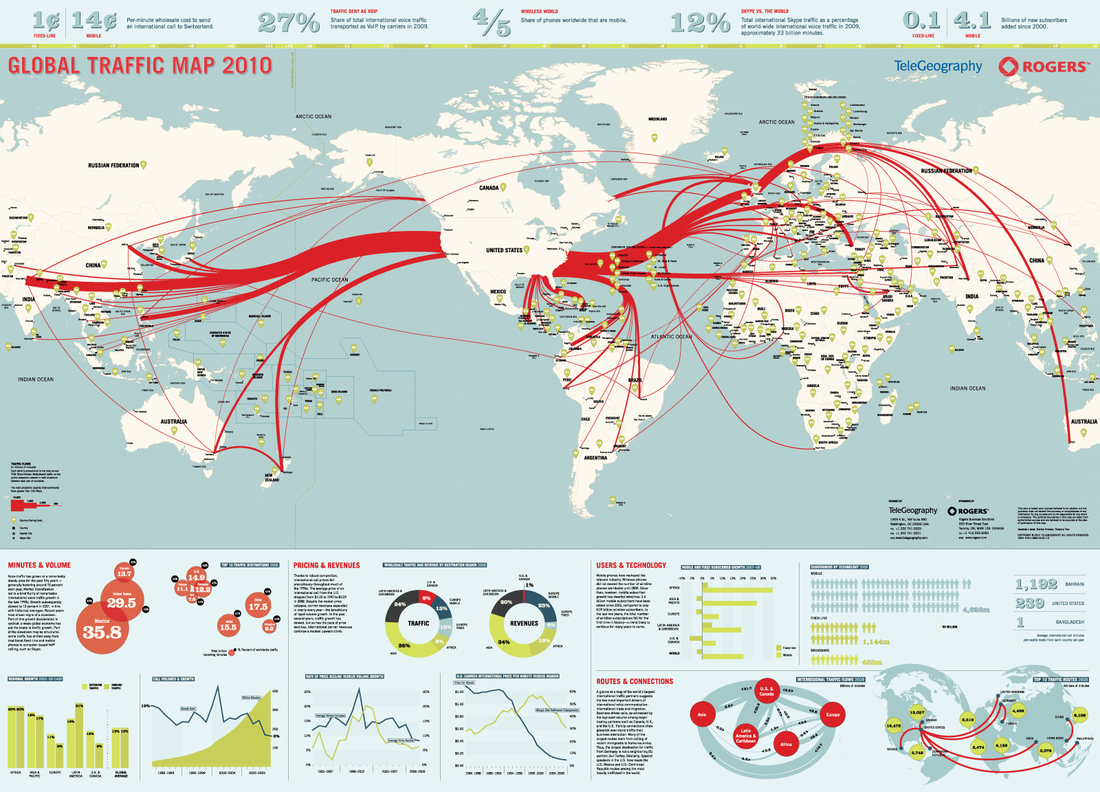
Information and the Internet
What is the internet and why has it grown? Watch the YouTube on the right and read the article from the Daily Mail. |
|
|
Describe the pattern of internet growth. Use the BBC Technology map and the image on the left.
|
The internet does not just exist as a 'cloud' concept it is based in physical technology and networks. Explain what this means and give examples.
|
|
|
Make notes on how the internet has changed the world:

IB Style Question:
Explain what the internet is and how it has further 'shrunk' the world. [10]
Explain what the internet is and how it has further 'shrunk' the world. [10]
|
|
|
The Spread of Mobile Phones

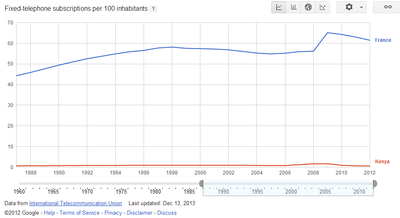
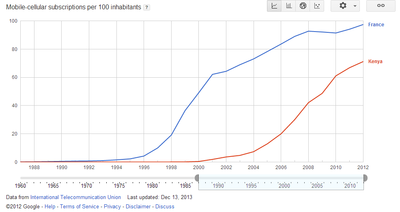
Case Study: Kenya Vs. France
|
Compare the top mobile phone using countries in the world. Pay especial attention to number of phones per 100 people. |

Watch the following two YouTubes and make notes on how mobile phones have changed over the last few years. What about Africa? What has been the impact on the African continent?
| Worksheet - The mobile phone industry over the years | |
| File Size: | 82 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
|
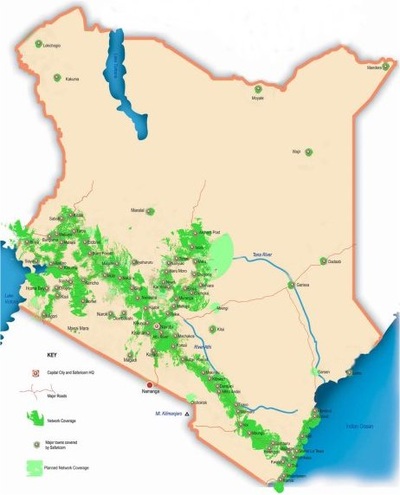
For further evidence on mobile phone penetration
|
|
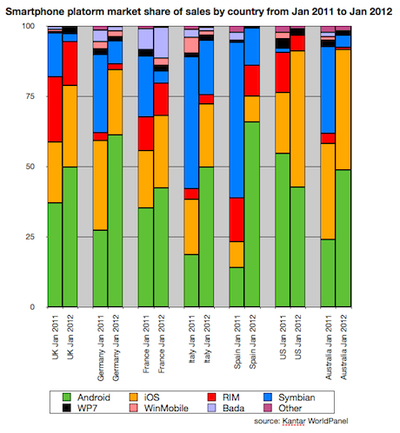
Use the Slide Share on the right to fill in this worksheet.
| |||||||
Make further notes using the following links and YouTubes:
|
|
|
Discuss the following graphs? Compare France to Kenya

IB Style Question:
Discuss how important the mobile phone has been to contributing to the reduction in frictional distance in the world [15]
Discuss how important the mobile phone has been to contributing to the reduction in frictional distance in the world [15]
|
|
|