Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| ecosystems.pdf | |
| File Size: | 139 kb |
| File Type: | |
Ecosystems and Biomes - Introduction
Ecosystems: A biological environment consisting of all the living organisms (biotic) within a particular area and the nonliving (abiotic) that interact with the organisms e.g. weather, soil, air and water.
Biome: Is a major ecological community with distinct climate, animals and plants. A biome is made of many similar ecosystems.
Biome: Is a major ecological community with distinct climate, animals and plants. A biome is made of many similar ecosystems.
We will be focusing on two Biomes.

Watch the following short explanation of Biomes and also explore the Biomes of the world on the following two links./
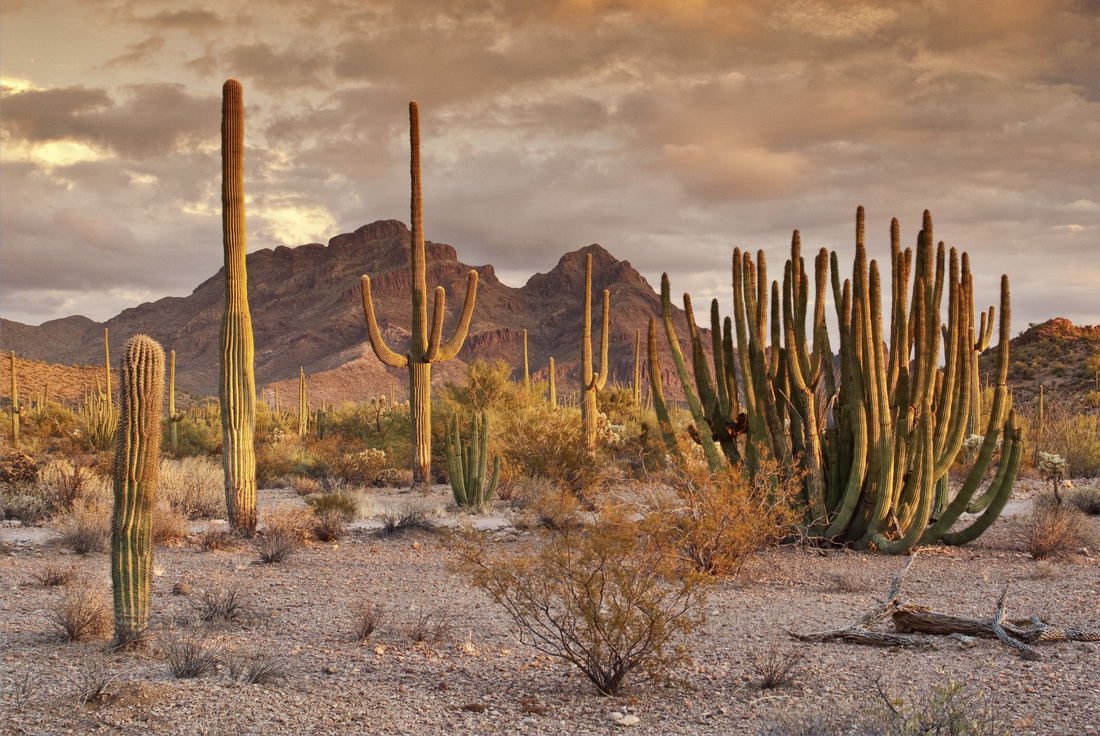
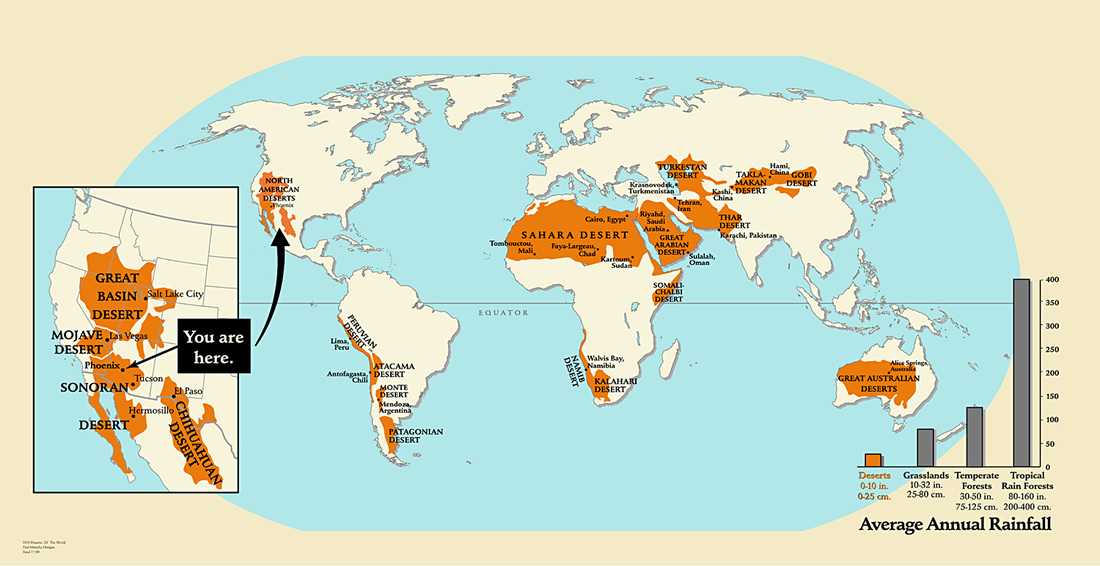
Hot Deserts

Complete the Desert location worksheet using the map above.
|
| ||||||
Why do Deserts Exist?
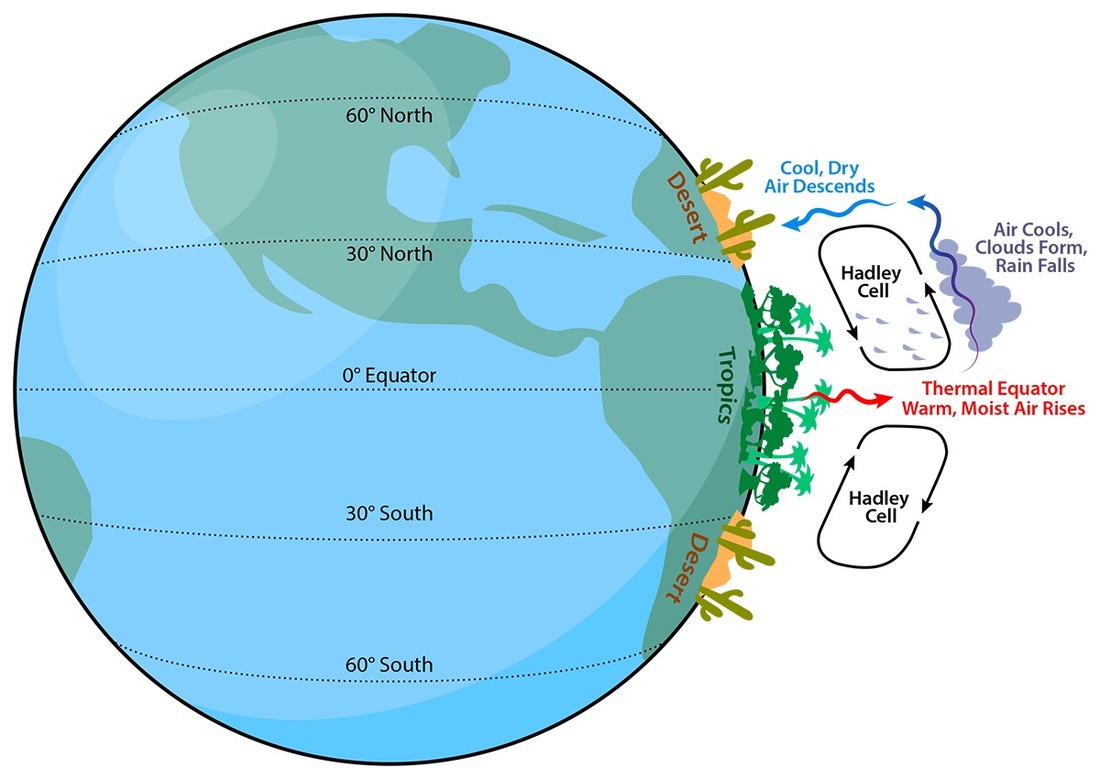
First REason - The Hadley Cell
The Hadley Cell
|
Drying Deserts with Air
Deserts cover around 20% of the Earth and are on every continent. They are mainly found around 30 to 50 degrees latitude, called the midlatitudes. These areas are about halfway between the equator and the north and south poles. Remember that moist, hot air always rises from the equator. As this air climbs higher in the sky, it cools. Cool air can hold less water than warm air. This means that as the air cools, clouds form that release most of the water they hold. Because the cooling air is above the equator, the moisture rains back down on the tropics. As warm air keeps rising from the equator, it pushes the cooler air away. The cool air moves north and south before falling back toward the ground at around 30 to 50 degrees north and south of the equator. With warm air rising above the equator and the cooled air falling to the north and south, two circular patterns of air movement are created around the equator. These patterns of air circulation are called Hadley cells. When the cool air begins to fall back toward the ground, or descend, it starts to warm up again. This warm, dry air can hold a lot of water, so the air starts to suck up what little water is around. At 30 to 50 degrees north and south of the equator, this falling air makes dry air drier. It also turns the land below it into a desert. |
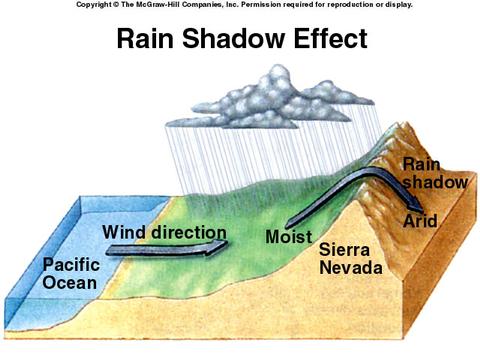
Second REason - The Rain Shadow effect
The Rain shadow Effect
|
As we have seen in the first reason sinking air is cooler and drier than rising air and therefore all areas of desert are under persistent High air pressure.
The driest deserts on our planet are found in these areas. For example the Atacama desert in South America is found in the rain shadow of the Andes Mountain Range. Water comes off the Pacific Ocean, it hits the Andes range, gets pushed up and empties all its water on the West side of the range. After it passes over the top it begins to sink and warm pulling in all moisture around it causing a desert to form. |
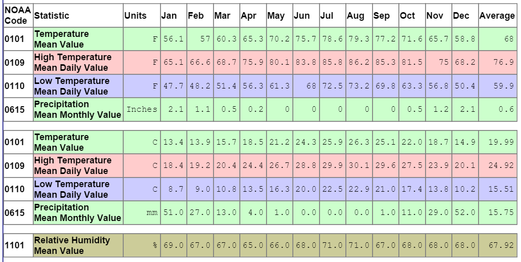
What is the Climate Like?

Using the Average Climate data for Alexandria below, complete the Climograph. |
| ||||||
Plant and Animal Adaptations

The best way to examine how animals and plants adapt to the desert environment is to see them! We will be watching the BBC Documentary: Planet Earth - Deserts to do this. You will need to complete the attached table whilst watching this documentary.
| Adaptations Table | |
| File Size: | 88 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
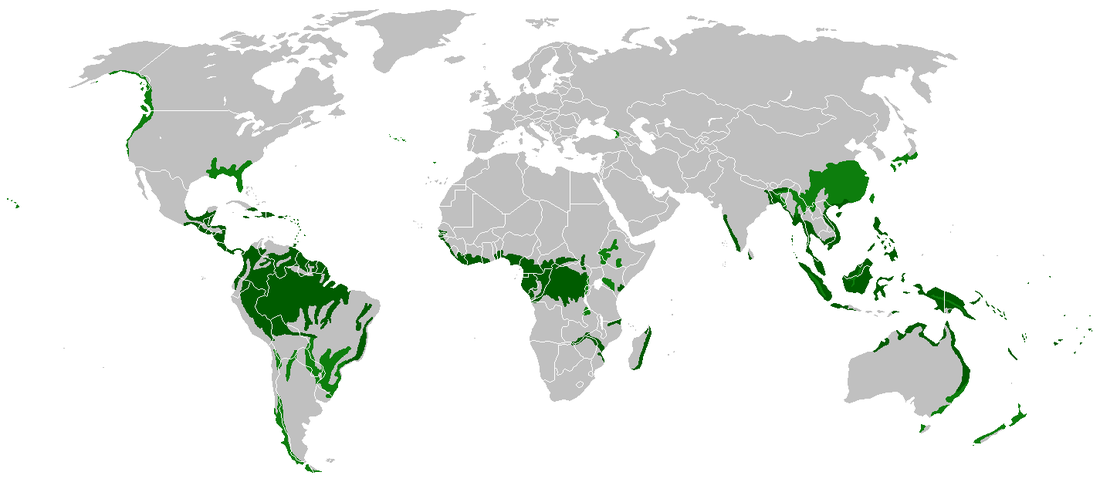
Tropical Equatorial Rainforests

Complete the Rainforest location worksheet using the map above. |
| ||||||
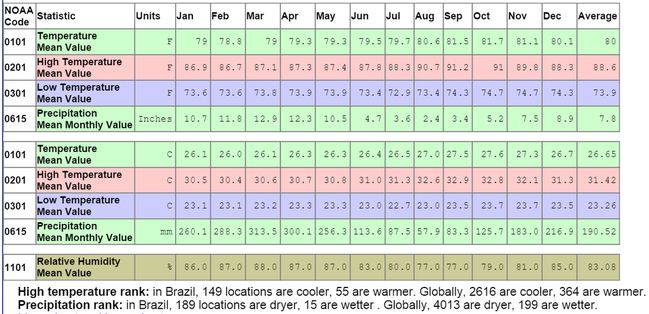
What is the climate like?

Using the Average Climate data for Manaus below, complete the Climograph.
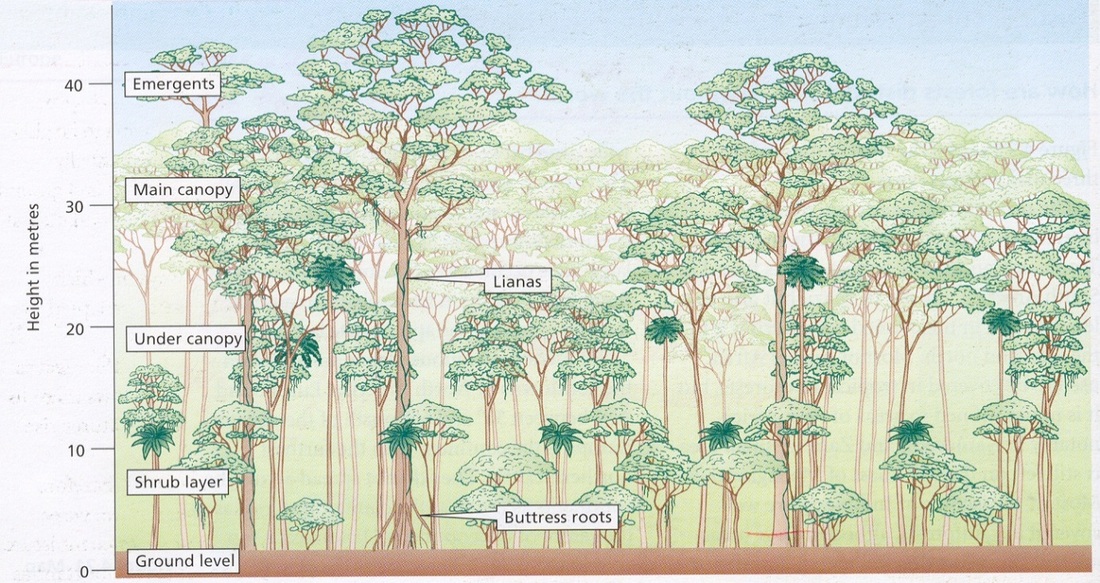
What does a rainforest look like?
Plant and Animal Adaptations

The best way to examine how animals and plants adapt to the desert environment is to see them! We will be watching the BBC Documentary: Planet Earth - Jungles to do this. You will need to complete the attached table whilst watching this documentary.
| Plant and Animal Adaptations Worksheet | |
| File Size: | 88 kb |
| File Type: | docx |
Case Studies
Case Study: Sahel (Africa) and Amazon (Brazil)
This case study will be created as a presentation. You will be working in groups to create a presentation in which you will answer the following questions.
This case study will be created as a presentation. You will be working in groups to create a presentation in which you will answer the following questions.
- Locate your area (where is it, region, major cities, rivers etc)
- Why is this region?
- Desertification (Sahel)
- Tropical Rainforest (Amazon)
- Give some specific examples of plants and animals that live here and how they have adapted.
- What human activities are occurring in the area?
- How are human activities harming the environment?
- What are we doing to help protect these environments?