Pro/ Anti-Natalist policiesThese policies are created by the government to monitor young dependents population. If a country has too many young born compared to the economically active part, then if not controlled it could have a negative impact on the society and economy of the country. Like in China where a baby boom has been witnessed, the government had to do something so that the number of babies being born decreased. if this was to continu it would have a negative impact on government spending, therefore it would cost too much for population to have healthcare.
However, if a country has too few children then a pro natalist policy should be introduced so that when the economically active part goes to old dependent then the young ones will take the lead but if they are too few then the economy of the country will suffer because less pension for old and less healthcare for younger due to less people paying taxes in the economical active part. |
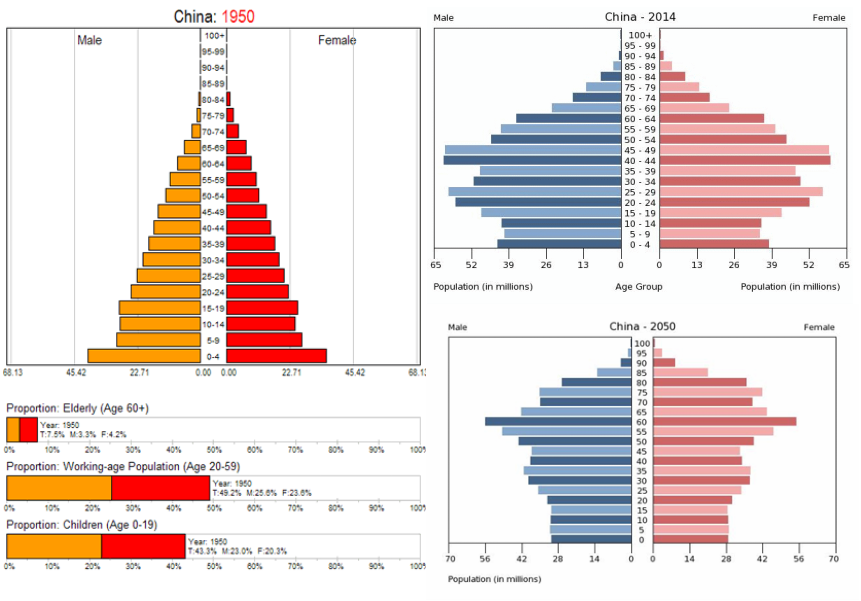
Background of China
- In 1950 Chinas population increased by 1.9% each years but if nothing changes the population will double in 24 years.
- One child policy was introduced otherwise it would be unsustainable for China to continue the way it was doing.
One child policy
Part1
- In 1979 china decreed one child policy and its benefits to couple who had one child per family
- If the rules were followed the couple could have an increase access to education for all, more childcare, and healthcare.
- In can increase the food supply
- It can result in more resources for children development
- Better health care for families
- Overall better living standards
- Increased saving rate: the average family expends fewer resources due to fewer children
- Maintaining a steady labor rate
- Reduces unemployment (more jobs available due to decrease in population)
Part2
- Those who had more than one child could get those benefits
- Hard to introduce one child policy to every part of china especially in rural
- Women who had already a child were sometime sterilize, or had to abort
- The first and second generation children wont have any siblings or first cousins.
- Gender Inequalities: women will continue to be looked as the lower sex in China; due to this many couples who have a baby girl sometimes kill or abandon their child
- Gender Imbalance: more men than women.
- Forced abortions and involuntary sterilization of mothers.
- Psychology of children: mainly all children are the only child in their families, and as result face more psychological problems without siblings
Part3
- the one child policy has been a success has the Chinese government says, the birth rate decreased to 1.5 birth which means that a women gives birth to 1.5 kids the 0.5 is from rural because they are allowed more if first born is girl.
More information about one child policy:
Other policies of anti natalist:
- A country like Singapore introduced the same policy as china did, however it didn’t steal all of its ideas, Such as low cost contraceptive, higher family planning aid, more advertisement and government help for small families. After this policy came the fertility rate dropped to 1.2 in 2011, but the old dependent will increase but however the huge young dependent has now came into economically active, therefore, the economy of the country is more likely to grow.
How was it before?
China was not always an anti-natalist. Between 1953 and 1964 China encouraged large families to make the country stronger and more powerful. It increased by 112 million. But then, in 1970, Mao Zedong encouraged to limit families to two children. The slogan “Later, Longer, Fewer” was the message passed around to balance out the population growth. Showing how serious they were, they introduced the one child policy in 1970.
Who does it affect?
- Only 35% of Chinas population is affected by china one child policy. An example could be in rural areas where farmers are allowed to have a maximum of two children if the first one is a girl so that the boy can help the father in the lands.
What about today ?
Thirty years later, the one child policy has relaxed quite a bit. They can also have a second child if just one of the parents was an only child. Today, China’s population is still increasing slowly with its total population of 1.4 billion but is being faced to some new issues, such as the falling birth rate and less amount of working people to support the dependent population. In the future, China might become an ageing population.